Mechanisms of Alpha-Synuclein-Seeded Aggregation in Neurons Revealed by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging
- PMID: 40421805
- PMCID: PMC12142570
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00236
Mechanisms of Alpha-Synuclein-Seeded Aggregation in Neurons Revealed by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging
Abstract
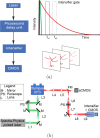
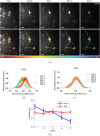
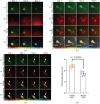
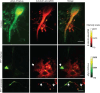
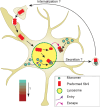
The brains of Parkinson's disease (PD) patients are characterized by the presence of Lewy body inclusions enriched with fibrillar forms of the presynaptic protein alpha-synuclein (aSyn). Despite related evidence that Lewy pathology spreads across different brain regions as the disease progresses, the underlying mechanism, and hence the fundamental cause of PD progression, is unknown. The propagation of aSyn pathology is thought to potentially occur through the release of aSyn aggregates from diseased neurons, their uptake by neighboring healthy neurons via endocytosis, and subsequent seeding of native aSyn aggregation in the cytosol. A critical aspect of this process is believed to involve the escape of internalized aggregates from the endolysosomal compartment, though direct evidence of this mechanism in cultured neuron models remains lacking. In this study, we utilize a custom-built, time-gated fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) system to investigate the progression of seeded aggregation over time in live cortical neurons. By establishing fluorescence lifetime sensitivity to aSyn aggregation levels, we are able to monitor the protein's aggregation state. Through a FLIM analysis of neurons expressing aSyn-mVenus and exposed to aSyn preformed fibrils labeled with the acid-responsive dye pHrodo, we reveal the protein's aggregation state in both the cytosol and the endolysosomal compartment. The results indicate that aSyn seeds undergo partial disassembly prior to escaping the endocytic pathway and that this escape is closely linked to the aggregation of cytosolic aSyn. In certain neurons, monomeric aSyn is found to translocate from the cytosol into the endolysosomal compartment, where it apparently forms aggregates in proximity to retained seeds. Additional analyses reveal zones of neuritic aSyn aggregates that overlap with regions of microtubule disruption. Collectively, these findings enhance our understanding of aSyn pathology propagation in PD and other synucleinopathies, motivate additional experiments along these lines, and offer a path to guide the development of disease-modifying therapies.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; alpha-synuclein; fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy; live-cell imaging; neurodegenerative diseases; protein aggregation.
Figures



Update of
-
Mechanisms of Alpha-Synuclein Seeded Aggregation in Neurons Revealed by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 17:2024.12.16.628520. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.16.628520. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Jun 4;16(11):2128-2140. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00236. PMID: 39763977 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Alpha-Synuclein Seeded Aggregation in Neurons Revealed by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 17:2024.12.16.628520. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.16.628520. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Jun 4;16(11):2128-2140. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00236. PMID: 39763977 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Do Lewy bodies contain alpha-synuclein fibrils? and Does it matter? A brief history and critical analysis of recent reports.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jul;141:104876. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104876. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32339655 Review.
-
Evidence for bidirectional and trans-synaptic parasympathetic and sympathetic propagation of alpha-synuclein in rats.Acta Neuropathol. 2019 Oct;138(4):535-550. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-02040-w. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Acta Neuropathol. 2019. PMID: 31254094 Free PMC article.
-
The small molecule alpha-synuclein misfolding inhibitor, NPT200-11, produces multiple benefits in an animal model of Parkinson's disease.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 1;8(1):16165. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34490-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30385782 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein Pathology in Synucleinopathies: Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 4;26(11):5405. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115405. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

