Percutaneous Bone Implant Surgery: A MIPS Modified Technique
- PMID: 40421845
- PMCID: PMC12371826
- DOI: 10.1002/lary.32192
Percutaneous Bone Implant Surgery: A MIPS Modified Technique
Abstract
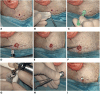
Since their introduction, passive percutaneous hearing aids have undergone substantial evolution, including changes in implant production, improvements in the sound processor, and simplification of surgical implantation techniques. The latest innovation comes from the minimally invasive technique proposed for the PONTO system (MIPS), which does not involve the creation of a mucoperiosteal flap in order to leave the surrounding soft tissue and vascular microcirculation intact. This study proposes a modified surgical technique compared to the one proposed for the PONTO system in order to overcome some steps of the traditional surgical technique for the placement of the Baha Connect prosthesis. Our technique does not involve any incision but the exposure of the periosteum using a skin punch and subsequent drilling without the use of any protective cannula. The described procedure allows one to overcome some steps of the traditional surgical technique and, consequently, also some post-operative complications. Moreover, a minimally invasive procedure can help reduce surgical time and the invasiveness of the application.
Keywords: bone; deafness; implants; percutaneous BCI.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Laryngoscope published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anterior Approach Total Ankle Arthroplasty with Patient-Specific Cut Guides.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2025 Aug 15;15(3):e23.00027. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.23.00027. eCollection 2025 Jul-Sep. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2025. PMID: 40821726 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of a New Minimally Invasive Single-Drill Procedure for Installing Percutaneous Bone-Anchored Hearing Implants in Adult Patients.Otol Neurotol. 2025 Jun 1;46(5):e190-e197. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000004484. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Otol Neurotol. 2025. PMID: 40062360 English, Portuguese.
-
Does Transhumeral Osseointegration After Amputation Improve Patient-reported Outcomes and Prosthesis Use?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Feb 19;483(8):1502-1510. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003420. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39982023
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: management of soft tissues for dental implants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Feb 15;2012(2):CD006697. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006697.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22336822 Free PMC article.
-
Punch vs open surgical techniques for placement of bone-anchored hearing implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis of skin reactions and operating time.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Sep;278(9):3171-3180. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06511-9. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33389004
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

