Principles for Dendritic Spine Size and Density in Human and Mouse Cortical Pyramidal Neurons
- PMID: 40421877
- PMCID: PMC12108034
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.70060
Principles for Dendritic Spine Size and Density in Human and Mouse Cortical Pyramidal Neurons
Abstract
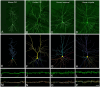
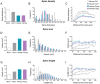
Dendritic spines of pyramidal neurons are the targets of most excitatory synapses in the cerebral cortex, and dendritic spine morphology directly reflects their function. However, there are scarce data available regarding both the detailed morphology of these structures for the human cerebral cortex and the extent to which they differ in comparison with other species. Thus, in the present study, we used intracellular injections of Lucifer yellow to reconstruct-in three dimensions-the morphology of basal dendritic spines from pyramidal cells in the human and mouse CA1 hippocampal region and compared these spines with those of the human temporal and cingular cortex. We found that human hippocampal dendrites show lower spine density, larger volume, and longer length of dendritic spines than mouse CA1 spines. Furthermore, human hippocampal dendrites show higher spine density, smaller spine volume, and shorter length compared to dendritic spines from the human temporal and cingular cortex. This morphological diversity suggests an equally large variability of synaptic strength and learning rules across these brain regions in humans and between humans and mice. Nevertheless, a balance between size and density was found in all cases, which may be a cortical rule maintained across cortical areas and species.
Keywords: 3D reconstructions; F factor; JEL Classification: RRID:AB_1062582; RRID:SCR_002798; RRID:SCR_007370; RRID:SCR_016788; RRID:SCR_017348; RRID:SCR_020233; cerebral cortex; dendrites; intracellular injections; morphology; pyramidal cells.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Journal of Comparative Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Age-based comparison of human dendritic spine structure using complete three-dimensional reconstructions.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Aug;23(8):1798-810. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs154. Epub 2012 Jun 17. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22710613 Free PMC article.
-
Density and morphology of dendritic spines in mouse neocortex.Neuroscience. 2006;138(2):403-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.11.038. Epub 2006 Feb 2. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16457955
-
Key morphological features of human pyramidal neurons.Cereb Cortex. 2024 May 2;34(5):bhae180. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae180. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 38745556 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Golgi-Cox and Intracellular Loading of Lucifer Yellow for Dendritic Spine Density and Morphology Analysis in the Mouse Brain.Neuroscience. 2022 Aug 21;498:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.029. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 35752428 Free PMC article.
-
Structural dynamics of dendritic spines in memory and cognition.Trends Neurosci. 2010 Mar;33(3):121-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.01.001. Trends Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20138375 Review.
References
-
- Arellano, J. I. , Benavides‐Piccione R., DeFelipe J., and Yuste R.. 2007. “Ultrastructure of Dendritic Spines: Correlation Between Synaptic and Spine Morphologies.” Frontiers in Neuroscience 1, no. 1: 131–143. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/neuro.01.1.1.010.2007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arellano, J. I. , Espinosa A., Fairén A., Yuste R., and DeFelipe J.. 2007. “Non‐Synaptic Dendritic Spines in Neocortex.” Neuroscience 145: 464–469. - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros‐Yáñez, I. , Benavides‐Piccione R., Bourgeois J.‐P., Changeux J.‐P., and DeFelipe J.. 2010. “Alterations of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons in Mice Lacking High‐Affinity Nicotinic Receptors.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107: 11567–11572. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros‐Yáñez, I. , Benavides‐Piccione R., Elston G. N., Yuste R., and DeFelipe J.. 2006. “Density and Morphology of Dendritic Spines in Mouse Neocortex.” Neuroscience 138: 403–409. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

