Neurometabolite Alterations Associated With Cannabis Use: A Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40421881
- PMCID: PMC12107604
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.70236
Neurometabolite Alterations Associated With Cannabis Use: A Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Meta-Analysis
Abstract
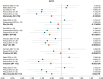
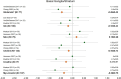
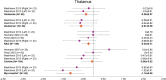
Little is known about the neurometabolic effects of cannabis use. Using meta-analytic modeling of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) studies, this study aimed to assess the differences in brain metabolite levels associated with cannabis use (PROSPERO: CRD42020209890) to inform treatment development for cannabis use disorder (CUD). Hedge's g with random-effects modeling was used, and heterogeneity and publication bias indices were assessed. A complete literature search was conducted, and 15 studies met the inclusion criteria (e.g., 1H-MRS, cannabis group compared to a control group, brain region-specific results, necessary data to complete modeling). There were 29 models across gray matter regions in the brain. All models had between 2 and 5 studies (k), indicating that results should be interpreted with caution due to the limited number of available studies. Compared to the control groups, the cannabis-using groups showed lower levels of GABA and N-acetylaspartate in the anterior cingulate cortex (k = 3); lower glutamate in the basal ganglia/striatum (k = 2); and lower glutamine and myo-inositol in the thalamus (k = 2; although the two effect sizes came from the same sample). This is the first meta-analysis to consolidate the extant 1H-MRS studies focused on the neurometabolic effects of cannabis. Despite the few studies available, the evidence suggests cannabis use may impact important neural processes, including glutamatergic and GABAergic functioning (glutamate, glutamine, and GABA), neural health (N-acetylaspartate), and glial functioning (myo-inositol). The findings should be interpreted with caution considering the small sample size; the inability to test the impact of demographic, substance use, and methodological factors; and the heterogeneity of studies. Understanding the neurobiological effects of cannabis may inspire novel pharmacotherapy and/or psychosocial interventions for CUD.
Keywords: cannabis use disorder; meta‐analysis; neurometabolites; proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy; substance use disorders.
© 2025 The Author(s). Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antenatal dietary supplementation with myo-inositol in women during pregnancy for preventing gestational diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 17;2015(12):CD011507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 15;2:CD011507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011507.pub3. PMID: 26678256 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Psychosocial interventions for cannabis use disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD005336. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005336.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149547 Free PMC article.
-
[Cannabis and psychosis: search of a causal link through a critical and systematic review].Encephale. 2009 Sep;35(4):377-85. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.02.012. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19748375 French.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Pharmacotherapy for anxiety and comorbid alcohol use disorders.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 20;1(1):CD007505. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007505.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25601826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel‐Salam, O. M. 2022. “The Neurotoxic Effects of Cannabis on Brain: Review of Clinical and Experimental Data.” Molecular Sciences and Applications 2: 11–23.
-
- Bakhshinezhad, H. , Darharaj M., Feyzi Y. F., et al. 2022. “The Relationship Between Brain Metabolites Alterations and Neuropsychological Deficits in Patients With Methamphetamine Use Disorder: A Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study.” Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 37, no. 1: 160–172. - PubMed
-
- Barantin, L. , Pape A. L., and Akoka S.. 1997. “A New Method for Absolute Quantitation MRS Metabolites.” Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 38, no. 2: 179–182. - PubMed
-
- Blest‐Hopley, G. , O'Neill A., Wilson R., et al. 2020. “Adolescent‐Onset Heavy Cannabis Use Associated With Significantly Reduced Glial but Not Neuronal Markers and Glutamate Levels in the Hippocampus.” Addiction Biology 25, no. 6: e12827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

