Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Ricin in Biological Fluids Using Optical Modulation Biosensing
- PMID: 40422034
- PMCID: PMC12109947
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15050295
Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Ricin in Biological Fluids Using Optical Modulation Biosensing
Abstract
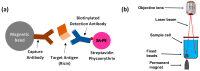
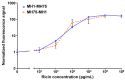
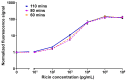
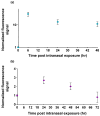
Ricin, a highly toxic glycoprotein derived from the seeds of Ricinus communis, poses significant risks in bioterrorism and toxicology due to its rapid absorption and ease of dissemination. Rapid, ultra-sensitive detection is crucial for timely medical intervention and implementing security measures. However, existing methods often lack sufficient sensitivity or require lengthy processing, limiting their utility for trigger-to-treat scenarios. Here, we present an optical modulation biosensing (OMB)-based ricin assay capable of detecting low concentrations of ricin in buffer, plasma, and biological samples. The assay combines magnetic-bead-based target capture with fluorescent signal enhancement, achieving a limit of detection (LoD) of 15 pg/mL in buffer and 62 pg/mL in plasma, with a 4-log dynamic range. Optimized protocols reduced the assay time to 60 min, maintaining an LoD of 114 pg/mL in plasma while preserving accuracy and reproducibility. The assay successfully detected ricin in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and serum from mice that were intranasally exposed to ricin, with signals persisting up to 48 h post exposure. Its rapid, high-throughput capabilities and simplified workflow make the OMB-based assay a powerful tool for toxicology, forensic analysis, and counter-bioterrorism. This study highlights the OMB platform's potential as a sensitive and robust diagnostic tool for detecting hazardous biological agents.
Keywords: bioterrorism; fluorescence-based immunoassay; optical modulation biosensing; ricin; toxicology diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
A.D. has a financial interest in MagBiosense, Inc., which, however, did not financially support this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid, Sensitive and Reliable Ricin Identification in Serum Samples Using LC-MS/MS.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 22;13(2):79. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020079. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33499033 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Detection of Ricin in Serum Based on Cu-Chelated Magnetic Beads Using Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2016 Apr;27(4):748-51. doi: 10.1007/s13361-016-1340-1. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2016. PMID: 26873724
-
Ricin toxicokinetics and its sensitive detection in mouse sera or feces using immuno-PCR.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 22;5(9):e12858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012858. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20877567 Free PMC article.
-
[Highly toxic type Ⅱ ribosome-inactivating proteins ricin and abrin and their detection methods: a review].Se Pu. 2021 Mar;39(3):260-270. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.10001. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227307 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Ricinus communis intoxications in human and veterinary medicine-a summary of real cases.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Oct;3(10):1332-72. doi: 10.3390/toxins3101332. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neagu M., Constantin C., Del Gaudio P., Garcia-Gonzalez C.A. Chapter 17—Updates on current biomarkers in toxicology. In: Tsatsakis A.M., editor. Toxicological Risk Assessment and Multi-System Health Impacts from Exposure. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2021. pp. 191–204. - DOI
-
- Perlin D. Beyond Anthrax: The Weaponization of Infectious Diseases. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ, USA: 2008. Rapid Detection of Bioterrorism Pathogens.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

