Probing the Influence of Specular Reflection and Overexposure on Backscattering Mueller Matrix Polarimetry for Tissue Imaging and Sensing
- PMID: 40422072
- PMCID: PMC12110177
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15050333
Probing the Influence of Specular Reflection and Overexposure on Backscattering Mueller Matrix Polarimetry for Tissue Imaging and Sensing
Abstract
Mueller matrix polarimetry has great potential for tissue detection and clinical diagnosis due to its ability to provide rich microstructural information accurately. However, in practical in vivo tissue imaging based on backscattering Mueller matrix polarimetry, specular reflection is often inevitable, leading to overexposed regions and the following inaccurate polarization information acquisition of tissues. In this study, we probe the influence of specular reflection and overexposure on backscattering Mueller matrix polarimetry for tissue imaging and sensing. We investigate in detail the differentiation of polarization behaviors between the specular reflection and non-specular reflection tissue regions using a 3 × 3 backscattering Mueller matrix measurement. Then, we obtain the vertical projection profiles to further quantify the Mueller matrix elements of porcine liver tissue in different specular reflection regions. Finally, we calculate the polarization feature parameters derived from a 3 × 3 Mueller matrix and analyze their behavior in overexposed regions. Based on the quantitative analysis and comparisons, we obtain a group of polarization feature parameters with strong immunity to the specular reflection process. This study offers a strategy for selecting the polarization parameters during in vivo polarimetric imaging applications, provides valuable references for further eliminating the characterization errors induced by specular reflection, and may contribute to the advancement of quantitative tissue polarimetric imaging and sensing.
Keywords: Mueller matrix; overexposure; polarimetry; tissue imaging and sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this paper.
Figures

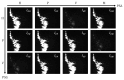
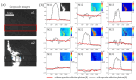

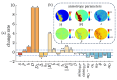
Similar articles
-
Complex Spatial Illumination Scheme Optimization of Backscattering Mueller Matrix Polarimetry for Tissue Imaging and Biosensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 22;14(4):208. doi: 10.3390/bios14040208. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667201 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and optimization of the pixel saturation effect on backscattering Mueller matrix polarimetry.Opt Lett. 2025 Aug 15;50(16):5069-5072. doi: 10.1364/OL.567394. Opt Lett. 2025. PMID: 40815741
-
Comparative study of the imaging contrasts of Mueller matrix derived parameters between transmission and backscattering polarimetry.Biomed Opt Express. 2018 Aug 22;9(9):4413-4428. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.004413. eCollection 2018 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2018. PMID: 30615708 Free PMC article.
-
Mueller polarimetric imaging for surgical and diagnostic applications: a review.J Biophotonics. 2017 Aug;10(8):950-982. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201600152. Epub 2017 May 2. J Biophotonics. 2017. PMID: 28464464 Review.
-
Polarization-resolved Stokes-Mueller imaging: a review of technology and applications.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Sep;34(7):1283-1293. doi: 10.1007/s10103-019-02752-1. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30830559 Review.
References
-
- Ramella-Roman J.C., Saytashev I., Piccini M. A review of polarization-based imaging technologies for clinical and preclinical applications. J. Opt. 2020;22:123001. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/abbf8a. - DOI
-
- Tukimin S.N., Karman S.B., Ahmad M.Y., Zaman W.S.W.K. Polarized light-based cancer cell detection techniques: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019;19:9010–9025. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2924535. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

