Marine-Derived Compounds Combined with Nanoparticles: A Focus on the Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sector
- PMID: 40422797
- PMCID: PMC12113654
- DOI: 10.3390/md23050207
Marine-Derived Compounds Combined with Nanoparticles: A Focus on the Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sector
Abstract
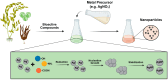
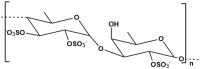
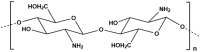
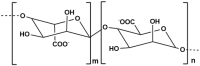
The ocean is an extraordinary natural source of a wide range of bioactive compounds. These compounds, including proteins, phenolics, polysaccharides, pigments, vitamins, and fatty acids, possess unique biological properties that are increasingly being explored in the field of nanotechnology across diverse sectors. Among marine-derived nanoparticles, promising applications have emerged in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields, particularly metallic nanoparticles and polysaccharide-based drug delivery systems. This review provides a unique perspective on the integration of two research areas: the exploration of marine bioresources as bioactive compounds sources with nanotechnological methodologies to develop sustainable, safe, stable and functional marine-derived NPs. It highlights recent advancements in the green synthesis of MNPs and the formulation of drug delivery systems using marine polysaccharides. This review also describes the recent trends over the past ten years and discusses the major challenges and limitations associated with these approaches, including variability in biological sources, batch-to-batch inconsistency, mechanistic uncertainties, and difficulties in reproducibility and scalability. Furthermore, it emphasizes the need for standardized protocols and the integration of life cycle assessments (LCA) to evaluate environmental and economic viability for effective translating marine-derives nanoparticles from research to clinical applications.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; green synthesis; marine bioactive compounds; marine polysaccharides; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Marine polysaccharide-based nanomaterials as a novel source of nanobiotechnological applications.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Jan;82:315-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.10.081. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 26523336 Review.
-
Marine polysaccharides from algae with potential biomedical applications.Mar Drugs. 2015 May 15;13(5):2967-3028. doi: 10.3390/md13052967. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25988519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field.Mar Drugs. 2019 Nov 21;17(12):654. doi: 10.3390/md17120654. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31766498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine-Derived Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Delivery Platforms for Natural Bioactive Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 17;26(2):764. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020764. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine algal polysaccharides for drug delivery applications: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Mar;295:139551. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.139551. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39778838 Review.
References
-
- Luzzatto-Knaan T., Garg N., Wang M., Glukhov E., Peng Y., Ackermann G., Amir A., Duggan B.M., Ryazanov S., Gerwick L., et al. Digitizing Mass Spectrometry Data to Explore the Chemical Diversity and Distribution of Marine Cyanobacteria and Algae. eLife. 2017;6:e24214. doi: 10.7554/eLife.24214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UIDB/00100/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/00100/2020) and UIDP/00100/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDP/00100/2020)/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT)
- LA/P/0056/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/LA/P/0056/2020)./Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT)
- UIDB/04138/2020, UIDP/04138/2020, UIDB/00645/2020 (https://doi. org/10.54499/UIDB/00645/2020) and UIDP/00645/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDP/00645/ 2020)./Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT)
- IPL/IDI&CA2024/SeaCoats_ISEL/Instituto Politécnico de Lisboa (IPL)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

