Codium fragile Extract Ameliorates Respiratory Function by Controlling Allergic Inflammation in Ovalbumin-Induced Bronchial Disorders in Mice
- PMID: 40422811
- PMCID: PMC12113249
- DOI: 10.3390/md23050221
Codium fragile Extract Ameliorates Respiratory Function by Controlling Allergic Inflammation in Ovalbumin-Induced Bronchial Disorders in Mice
Abstract
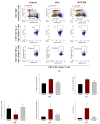
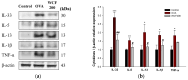
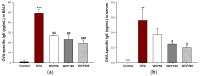
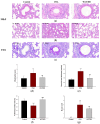
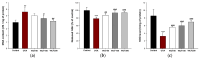
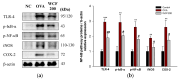
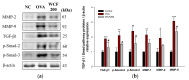
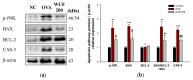
This study investigated the effect of Codium fragile (WCF) water extract in reducing allergic inflammation in ovalbumin (OVA)-induced mice. Mice were sensitized to OVA + aluminum hydroxide, administered WCF for one week, and exposed to 1% aerosolized OVA. As a result, WCF intake reduced the OVA-induced increase in CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, the T helper type 2 (Th2)/T helper type 1 (Th1) cell ratio, and inflammatory cells such as eosinophils and lymphocytes. Furthermore, WCF reduced Th2 cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-5, IL-13, and IL-33 and inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and IL-1β in lung tissues. A histological analysis showed that WCF intake decreases OVA-induced pulmonary inflammation, bronchial wall thickness, and mucus score and increases pulmonary alveolar area. Moreover, WCF inhibited the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/Smad pathway, and apoptosis-related proteins in lung tissues that OVA excessively activated. The oleamide (9-octadecenamide) content, representing a physiologically active component of WCF, was analyzed and validated using a high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array (HPLC-PDA) system. These results demonstrate that WCF may serve as a potential preventive agent for respiratory dysfunction such as allergic asthma by suppressing NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad pathways.
Keywords: Codium fragile; Th2 cytokine; allergic inflammation; fibrosis; oleamide; pulmonary function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gentiopicroside ameliorates ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma via regulating SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jun;68:102034. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2021.102034. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33887491
-
Vitex negundo Linn. extract alleviates inflammatory aggravation and lung injury by modulating AMPK/PI3K/Akt/p38-NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad/Bcl2/caspase/LC3 cascade and macrophages activation in murine model of OVA-LPS induced allergic asthma.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 May 10;271:113894. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113894. Epub 2021 Jan 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33516930
-
Bupleurum chinense extract ameliorates an OVA-induced murine allergic asthma through the reduction of the Th2 and Th17 cytokines production by inactivation of NFκB pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:1085-1095. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.133. Epub 2017 May 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28531919
-
Callicarpa japonica Thunb. ameliorates allergic airway inflammation by suppressing NF-κB activation and upregulating HO-1 expression.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113523. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113523. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33129947
-
Epimedin C modulates the balance between Th9 cells and Treg cells through negative regulation of noncanonical NF-κB pathway and MAPKs activation to inhibit airway inflammation in the ovalbumin-induced murine asthma model.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec;65:102005. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2021.102005. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33636365
References
-
- Wang M.-C., Huang W.-C., Chen L.-C., Yeh K.-W., Lin C.-F., Liou C.-J. Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora flavescens ameliorates allergic airway inflammation by suppressing Th2 response and oxidative stress in a murine asthma model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:6104. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

