Lipid Subclasses Differentiate Insulin Resistance by Triglyceride-Glucose Index
- PMID: 40422918
- PMCID: PMC12113954
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo15050342
Lipid Subclasses Differentiate Insulin Resistance by Triglyceride-Glucose Index
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance is a key driver of metabolic syndrome and related disorders, yet its underlying metabolic alterations remain incompletely understood. The Triglyceride-Glucose (TyG) index is an emerging, accessible marker for insulin resistance, with growing evidence supporting its clinical utility. This study aimed to characterize the metabolic profiles associated with insulin resistance using the TyG index in a large, population-based cohort, and to identify metabolic pathways potentially implicated in insulin resistance.
Methods: Here, we conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the Qatar Biobank, including 1255 participants without diabetes classified as insulin-sensitive or insulin-resistant based on TyG index tertiles. Untargeted serum metabolomics profiling was performed using high-resolution mass spectrometry. Our statistical analyses included orthogonal partial least squares discriminate analysis and linear models.
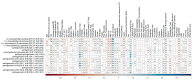
Results: Distinct metabolic signatures differentiated insulin-resistant from insulin-sensitive participants. Phosphatidylethanolamines, phosphatidylinositols, and phosphatidylcholines, were strongly associated with insulin resistance, while plasmalogens and sphingomyelins were consistently linked to insulin sensitivity.
Conclusions: Lipid-centric pathways emerge as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for the early detection and personalized management of insulin resistance and related metabolic disorders. Longitudinal studies are warranted to validate causal relationships.
Keywords: glycerophospholipids; metabolomics; plasmalogens; sphingomyelins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association Between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025 Apr;8(4):e70194. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70194. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40195579 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics of Lean/Overweight Insulin-Resistant Females Reveals Alterations in Steroids and Fatty Acids.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jan 23;106(2):e638-e649. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa732. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33053159
-
Association of the insulin resistance marker triglyceride glucose index with migraine: results of a cross-sectional and prospective cohort study.J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2025 Mar;39(1):165-175. doi: 10.22514/jofph.2025.017. Epub 2025 Mar 12. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2025. PMID: 40129435 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the triglyceride glucose index as a measure of insulin resistance with mortality and cardiovascular disease in populations from five continents (PURE study): a prospective cohort study.Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023 Jan;4(1):e23-e33. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00247-1. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023. PMID: 36521498
-
The role of the triglyceride-glucose index as a biomarker of cardio-metabolic syndromes.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Dec 23;23(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02412-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39716258 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

