3D-NASE: A Novel 3D CT Nasal Attention-Based Segmentation Ensemble
- PMID: 40423005
- PMCID: PMC12112669
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging11050148
3D-NASE: A Novel 3D CT Nasal Attention-Based Segmentation Ensemble
Abstract
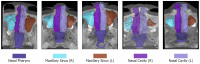
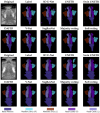
Accurate segmentation of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses in CT scans is crucial for disease assessment, treatment planning, and surgical navigation. It also facilitates the advanced computational modeling of airflow dynamics and enhances endoscopic surgery preparation. This work presents a novel ensemble framework for 3D nasal CT segmentation that synergistically combines CNN-based and transformer-based architectures, 3D-NASE. By integrating 3D U-Net, UNETR, Swin UNETR, SegResNet, DAF3D, and V-Net with majority and soft voting strategies, our approach leverages both local details and global context to improve segmentation accuracy and robustness. Results on the NasalSeg dataset demonstrate that the proposed ensemble method surpasses previous state-of-the-art results by achieving a 35.88% improvement in the DICE score and reducing the standard deviation by 4.53%. These promising results highlight the potential of our method to advance clinical workflows in diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical navigation while also promoting further research into computationally efficient and highly accurate segmentation techniques.
Keywords: 3D CT segmentation; 3D U-Net; Swin UNETR; UNETR; ensemble methods; nasal CT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shang Y., Inthavong K. Numerical assessment of ambient inhaled micron particle deposition in a human nasal cavity. Exp. Comput. Multiph. Flow. 2019;1:109–115. doi: 10.1007/s42757-019-0015-0. - DOI
-
- Pourmehran O., Psaltis A., Vreugde S., Zarei K., Shang Y., Inthavong K., Wormald P. Evaluating nebulisation and nasal irrigation efficiency in post-operative chronic rhinosinusitis patients through computational fluid dynamics simulation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025;264:108697. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2025.108697. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jing H., Cui X. A review on numerical studies of airflow dynamics and particle deposition in human respiratory system. Particuology. 2024;91:351–377. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2024.04.006. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

