A Review of Nanowire Devices Applied in Simulating Neuromorphic Computing
- PMID: 40423114
- PMCID: PMC12114477
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15100724
A Review of Nanowire Devices Applied in Simulating Neuromorphic Computing
Abstract
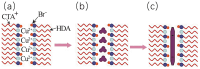
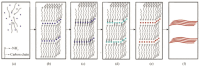
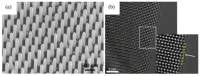
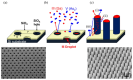
With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, the demand for enhanced device computing capabilities has significantly increased. Neuromorphic computing, an emerging computational paradigm inspired by the human brain, has garnered growing attention as a promising research frontier. Inspired by the human brain's functionality, this technology mimics the behavior of neurons and synapses to enable efficient, low-power computing. Unlike conventional digital systems, this approach offers a potentially superior alternative. This article delves into the application of nanowire materials (and devices) in neuromorphic computing simulations: First, it introduces the synthesis and preparation methods of nanowire materials. Then, it analyzes in detail the key role of nanowire devices in constructing artificial neural networks, especially their advantages in simulating the functions of neurons and synapses. Compared with traditional silicon-based material devices, it focuses on how nanowire devices can achieve higher connection density and lower energy consumption, thereby enabling new types of neuromorphic computing. Finally, it looks forward to the application potential of nanowire devices in the field of future neuromorphic computing, expecting them to become a key force in promoting the development of intelligent computing, with extensive application prospects in the fields of informatics and medicine.
Keywords: nanowire devices; neural network; neuromorphic computing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

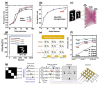
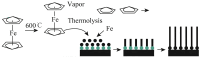
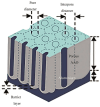

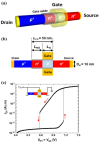
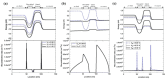
Similar articles
-
Advancements in Nanowire-Based Devices for Neuromorphic Computing: A Review.ACS Nano. 2024 Nov 19;18(46):31632-31659. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c10170. Epub 2024 Nov 5. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39499041 Review.
-
Multifunctional Organic Materials, Devices, and Mechanisms for Neuroscience, Neuromorphic Computing, and Bioelectronics.Nanomicro Lett. 2025 May 8;17(1):251. doi: 10.1007/s40820-025-01756-7. Nanomicro Lett. 2025. PMID: 40338405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermal Management in Neuromorphic Materials, Devices, and Networks.Adv Mater. 2023 Sep;35(37):e2205098. doi: 10.1002/adma.202205098. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 36067752 Review.
-
Electrolyte Gated Transistors for Brain Inspired Neuromorphic Computing and Perception Applications: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Feb 24;15(5):348. doi: 10.3390/nano15050348. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40072151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bio-Plausible Multimodal Learning with Emerging Neuromorphic Devices.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(45):e2406242. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406242. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39258724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schlatterer K. Universität Tübingen; Tübingen, Germany: 2022. Immune modulation by molecules of Staphylococcus aureus.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

