Bongkrekic Acid and Its Novel Isomers: Separation, Identification, and Determination in Food Matrices
- PMID: 40423306
- PMCID: PMC12115625
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins17050223
Bongkrekic Acid and Its Novel Isomers: Separation, Identification, and Determination in Food Matrices
Abstract
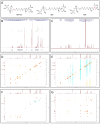
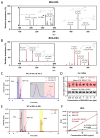
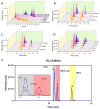
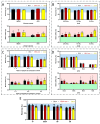
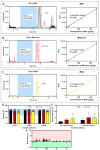
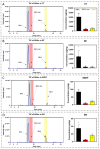
The toxicity associated with bongkrekic acid (BKA) is severe due to its chemical structure, which also facilitates high mortality rates; however, its isomer, isobongkrekic acid (iBKA), with only minor structural variance, demonstrates marked differences in toxicity. This discrepancy in structural properties and toxicity highlights that risks have been potentially underestimated within current detection standards for BKAs. In this study, a novel BKA trans isomer at the C8 and C9 double carbon bonds (E-configuration), termed iBKA-neo, was successfully separated and identified. Subsequently, the multiple reaction monitoring parameters and chromatographic conditions for three BKA isomers were optimized, enabling effective separation within 15 min via UHPLC-MS/MS, among which the ammonium positive adduct ions yielded significantly higher response intensities for all BKA isomers than traditional deprotonated molecules. Additionally, distinct differences in the ion ratios between iBKA-neo and BKA were utilized for preliminary screening. On this basis, the extraction and enrichment strategies for BKAs were optimized in food matrices and validated comprehensively with good linearity (0.25-500 μg/kg), a superior limit of quantification (0.25 μg/kg), acceptable recoveries (82.32-114.84%), and stable intraday and interday precision (an RSD less than 12.67%). These findings significantly contribute to ecotoxicology and the formulation of safety standards concerning BKAs.
Keywords: Burkholderia gladioli; UHPLC-MS/MS; biotoxin; bongkrekic acid; cis–trans isomer; food matrix.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Determination of bongkrekic acid in tremella and auricularia auricular by improved QuEChERS method combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2021 Dec;39(12):1368-1373. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.06013. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34812010 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Determination of bongkrekic acid and isobongkrekic acid in rice noodles by HPLC-Orbitrap HRMS technology using magnetic halloysite nanotubes.Food Chem. 2021 May 15;344:128682. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128682. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33246684
-
[Accurate determination of three new antihypertensive drugs illegally added to food using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2024 Oct;42(10):954-962. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.02025. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 39327659 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Bongkrekic Acid and Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans: Formidable Foe and Ascending Threat to Food Safety.Foods. 2023 Oct 26;12(21):3926. doi: 10.3390/foods12213926. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37959045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection methods and control measures of Burkholderia gladioli and its toxins: A review.J Food Sci. 2025 Feb;90(2):e17668. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.17668. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 39902981 Review.
References
-
- Li J., Zhou L.U., Long C., Fang L., Chen Q., Chen Q., Liang J., Yang Y., Zhu H., Chen Z., et al. An Investigation of Bongkrekic Acid Poisoning Caused by Consumption of a Nonfermented Rice Noodle Product without Noticeable Signs of Spoilage. J. Food Prot. 2019;82:1650–1654. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-19-121. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jones C., Webster G., Mullins A.J., Jenner M., Bull M.J., Dashti Y., Spilker T., Parkhill J., Connor T.R., LiPuma J.J., et al. Kill and cure: Genomic phylogeny and bioactivity of Burkholderia gladioli bacteria capable of pathogenic and beneficial lifestyles. Microb. Genom. 2021;7:000515. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000515. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

