Toxin Accumulation, Distribution, and Sources of Toxic Xanthid Crabs
- PMID: 40423311
- PMCID: PMC12115796
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins17050228
Toxin Accumulation, Distribution, and Sources of Toxic Xanthid Crabs
Abstract
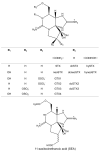
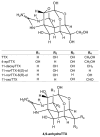
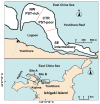
Several species of crabs from the Xanthidae family are recognized as dangerous marine organisms due to their potent neurotoxins, including paralytic shellfish toxin (PST), tetrodotoxin (TTX), and palytoxin (PLTX). However, the mechanisms of toxin accumulation and transport and the origin of these toxins in toxic xanthid crabs remain unknown. The identification of toxic crab species, their toxicity and toxin composition, and toxin profiles have been studied thus far. To date, more than ten species of xanthid crabs have been confirmed to possess toxins. Recently, several new studies on crabs, including the geographic distribution of toxin profiles and the ecological role of crabs, have been reported. Therefore, this review provides a summary of global research on toxic xanthid crabs, containing new findings and hypotheses on the toxification in and the origins of these crabs. Furthermore, the challenges and future perspectives in this field are also discussed.
Keywords: geographic distribution; origin; palytoxin; paralytic shellfish toxins; tetrodotoxin; toxic xanthid crabs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Noguchi T., Arakawa O., Daigo K., Oikawa H., Asakawa M., Miyazawa K. Chapter 36—Different intoxication mechanism between paralytic shellfish toxin (PST)- and/or tetrodotoxin-contaminated xanthid crabs and PST-contaminated edible shore crabs in Japan and their food poisonings. In: Konur O., editor. Handbook of Algal Science, Technology and Medicine. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2020. pp. 575–589.
-
- Hashimoto Y., KoNosu S., Inoue A., Saisho T., Miyake S. Screening of toxic crabs in the Ryukyu and Amami Islands. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1969;35:83–87. doi: 10.2331/suisan.35.83. - DOI
-
- Konosu S., Inoue A., Noguchi T., Hashimoto Y. A further examination on the toxicity of three species of xanthid crab. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1969;35:88–92. doi: 10.2331/suisan.35.88. - DOI
-
- Konosu S., Noguchi T., Hashimoto Y. Toxicity of a Xanthid Crab, Zosimus aeneus, and Several Other Species in the Pacific. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi. 1970;36:715–719. doi: 10.2331/suisan.36.715. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

