The Elias University Hospital Approach: A Visual Guide to Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Toxin Injection in Spasticity: Part III-Proximal Lower Limb Muscles
- PMID: 40423325
- PMCID: PMC12116053
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins17050240
The Elias University Hospital Approach: A Visual Guide to Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Toxin Injection in Spasticity: Part III-Proximal Lower Limb Muscles
Abstract
Ultrasound-guided botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) injections have become an essential tool in the management of lower limb spasticity. Following our previous work, which focused on upper limb muscles, this third part provides a detailed visual guide to the identification and injection of proximal lower limb muscles frequently involved in spastic gait and posture disorders. This guide presents the ultrasound anatomy, clinical relevance, and injection strategies for eleven key muscles: gluteusmaximus, piriformis, psoas major, rectusfemoris, sartorius, gracilis, adductorlongus, adductormagnus, semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and bicepsfemoris. For each muscle, the Elias University Hospital (EUH) model is applied, highlighting the zones of maximum thickness and motor point density to ensure precise and effective BoNT-A delivery. Enhanced with high-resolution ultrasound images and dynamic scanning techniques, this visual guide supports clinicians in performing safe, targeted injections. It serves as both an educational and practical reference for the ultrasound-guided treatment of spasticity in the proximal lower limb, completing the series and offering a standardized framework for comprehensive BoNT-A management. By promoting accurate toxin delivery, this approach is expected to improve functional mobility, reduce spasticity-related complications, and optimize patient-centered outcomes in rehabilitation settings.
Keywords: botulinum toxin-A injections; musculoskeletal ultrasound; post-stroke spasticity; proximal lower limb muscles; ultrasound-guided therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
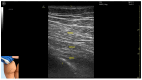
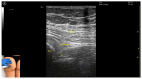
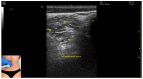
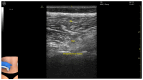
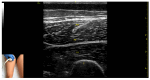
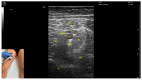
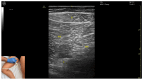
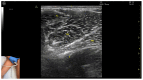
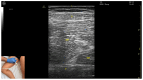
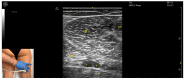
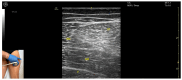
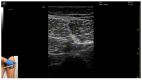
References
-
- Popescu M.N., Petca R.C., Beiu C., Dumitrascu M.C., Petca A., Mehedintu C., Farcasanu P.D., Sandru F. Efficiency of Different Preparations of Botulinum Toxin Type A, Xeomin and Dysport, in the Management of Spastic Upper Limb After Stroke. Revista de Chimie. 2019;70:3490–3494. doi: 10.37358/RC.19.10.7582. - DOI
-
- Faccioli S., Cavalagli A., Falocci N., Mangano G., Sanfilippo I., Sassi S. Gait Analysis Patterns and Rehabilitative Interventions to Improve Gait in Persons with Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2023;14:1256392. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1256392. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

