Botulinum Toxin in Pain-Related Post-Stroke Limb Spasticity: A Meta-Analysis of Early and Late Injections
- PMID: 40423340
- PMCID: PMC12116153
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins17050258
Botulinum Toxin in Pain-Related Post-Stroke Limb Spasticity: A Meta-Analysis of Early and Late Injections
Abstract
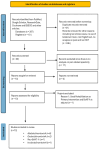
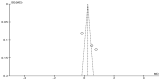
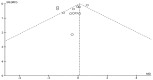
Spasticity is a common complication associated with stroke, and around 72% of stroke patients will develop pain during the disease. Botulinum toxin (BoNT) is a safe and efficacious treatment for spasticity and can improve associated complications, including pain. Hence, this meta-analysis aims to establish whether BoNT can reduce pain-related post-stroke spasticity (pPSS) in the early treatment period (<12 weeks post-stroke) or in the late period (>12 weeks post-stroke) based on the available evidence. This study also aims to establish the dose-response relationship of BoNT-A in pPSS. Based on pooled data from multiple studies, there is no significant difference in the scores measuring pPSS between patients who received early BoNT-A injections and those who received a placebo. This finding suggests that within the early treatment period, BoNT-A may not be more effective than a placebo in reducing pPSS. However, it is important to note that the data for early BoNT-A injections are limited, indicating that research is needed to draw definitive conclusions [z = 3.90 (p < 0.0001)]. While BoNT-A appears somewhat more effective than a placebo in the late phase, as indicated by the small to moderate positive z value, there is not enough evidence to confidently claim superiority over a placebo [z = 1.48 (p = 0.14)].
Keywords: botulinum toxin; early injection; late injection; pain-related post-stroke spasticity; spasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Stroke Organization World Stroke Organization Fact Sheet. 2022. [(accessed on 1 August 2024)]. Available online: https://www.world-stroke.org/assets/downloads/WSO_Global_Stroke_Fact_She....
-
- Biering-Soerensen B., Stevenson V., Bensmail D., Grabljevec K., Martínez Moreno M., Pucks-Faes E., Wissel J., Zampolini M. European Expert Consensus on Improving Patient Selection for the Management of Disabling Spasticity with Intrathecal Baclofen and/or Botulinum Toxin Type A. J. Rehabil. Med. 2022;54:jrm00241. doi: 10.2340/16501977-2877. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

