Integrin-fibronectin interaction is a pivotal biological and clinical determinant in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 40423510
- PMCID: PMC12150248
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-25-0101
Integrin-fibronectin interaction is a pivotal biological and clinical determinant in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Abstract
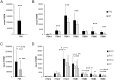
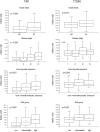
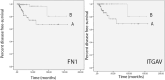
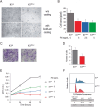
Integrins influence tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis, making them potential targets for therapeutic intervention. In this study, we analyzed the TCGA mRNA-seq dataset to assess the expression levels of fibronectin (FN1) and associated integrin subunits, evaluating their relationship with clinical features in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). These findings were further validated in a cell model. FN1 mRNA levels in BRAFV600E-positive PTC were 80-fold compared to normal thyroid tissue (NT), whereas PTC with RAS mutations exhibited FN1 levels similar to NT. ITGAV, encoding the αv integrin subunit, which pairs with β3 to form a receptor for FN, was also overexpressed in PTC. Elevated FN1 expression, and to a lesser extent ITGAV, correlated positively with lymph node metastasis, advanced cancer stages, extrathyroidal extension, and poorer prognoses. Patients in the highest quartile of FN1 expression had an increased risk of disease recurrence (OR = 7.277, 95% CI: 2.019-26.191, P < 0.0024). A non-tumoral thyroid cell line and two PTC cell lines were used as models to validate the mRNA-seq results. The proliferation and migration of a FN1 knock-out PTC cell mutant were significantly reduced and proliferation was restored upon the addition of soluble FN. DisBa-01, a recombinant RGD-disintegrin derived from Bothrops alternatus snake venom, which acts as an antagonist to the FN/αvβ3 interaction, inhibited PTC cell proliferation and migration. These results demonstrate that FN expression is a hallmark of aggressiveness in PTC. FN/αvβ3 interaction plays a pivotal role in PTC, suggesting that the FN/αvβ3 signaling is a potential therapeutic target for disintegrins or other molecules with similar action.
Keywords: disintegrins; fibronectin; integrins; thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the work reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FN1 shapes the behavior of papillary thyroid carcinoma through alternative splicing of EDB region.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83369-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747903 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-142-3P suppresses the progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting FN1 and inactivating FAK/ERK/PI3K signaling.Cell Signal. 2023 Sep;109:110792. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110792. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Cell Signal. 2023. PMID: 37406787
-
Oncogenic Ras/squamous cell carcinoma antigen signaling pathway activation promotes invasiveness and lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2019 Feb;41(2):1253-1263. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6895. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30535496
-
Functional Characterization of Plasminogen Activator Urokinase as a Key Gene in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Lymph Node Metastasis.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2025 Jun;29(6):152-165. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2025.0046. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2025. PMID: 40454923
-
TRIM29 inhibits miR-873-5P biogenesis via CYTOR to upregulate fibronectin 1 and promotes invasion of papillary thyroid cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Sep 29;11(9):813. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03018-3. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32994394 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

