Continuing medical education in epileptology: The Level 1-2-3 experience of the ILAE academy
- PMID: 40423759
- PMCID: PMC12574487
- DOI: 10.1002/epd2.70045
Continuing medical education in epileptology: The Level 1-2-3 experience of the ILAE academy
Abstract
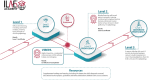
The International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) Academy is the world's eminent e-learning campus for epileptology. Its modular teaching content was developed to cover all competencies and learning objectives specified in the ILAE's curriculum for epileptology. The tutorless and self-paced entry Level 1 program for beginners offers an interactive case-based e-learning approach. A blended e-learning format was developed for the proficiency Level 2 with various learning domains and formats. They comprise a series of interactive, self-paced and case-based e-learning modules covering common, but also rare or complex epilepsy conditions, through state-of-the-art diagnosis and rational treatment decisions. Interactive EEG and MRI readers were integrated to support a tutorless online teaching format. An innovative adaptive e-learning format was applied for specific learning domains to reflect not only the proficiency level of the learner but also their self-confidence and perceived and unperceived knowledge of the topic. Our analysis of the completed adaptive e-learning courses revealed that 21% of the learning objectives had been answered incorrectly despite the learner indicating that they know the answer. This so-called "unconscious incompetence" should be regarded as a key motivation for building continuing medical education (CME) programs in epileptology. Level 2 utilizes a blended learning approach requiring 200 CME or equivalent ILAE credit points, earned through a mix of online learning with in-person participation in ILAE schools and congressional teaching activities. Level 3 is the subsequent step in the ILAE's structured learning path towards advanced proficiency and includes skill-based training in epileptology. Registered learners can apply for training visits in internationally renowned epilepsy centers around the world. Limited financial support is made available for selected applicants, e.g., to support candidates from resource limited settings. Designed to bridge the gap in knowledge and access to continuing education in epileptology, this unique structured learning path is open to all healthcare professionals.
Keywords: adaptive learning; antiseizure medication; brain; e‐learning; online learning; seizure.
© 2025 The Author(s). Epileptic Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
IB, EB, AAP, AA have nothing to disclose. CB has received support from and/or has served as a paid consultant for Angelini, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Marinus, and Xenon Pharma. JMW is an associate editor for Epilepsia. SW has received unrestricted educational grants on behalf of his institution from UCB Pharma, Sunovion, Eisai, Paladin Labs, and Jazz Pharma, and has received honoraria or served on advisory boards for Paladin Labs, Jazz Pharma, and Torrent Labs.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . Epilepsy fact sheet2024. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs999/en/
-
- Blümcke I, Arzimanoglou A, Beniczky S, Wiebe S. Roadmap for a competency‐based educational curriculum in epileptology: report of the Epilepsy Education Task Force of the International League Against Epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2019;21(2):129–140. - PubMed
-
- Beniczky S, Blümcke I, Rampp S, Shisler P, Biesel E, Wiebe S. E‐learning comes of age: web‐based education provided by the International League Against Epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2020;22(3):237–244. - PubMed
-
- Knowles MS. Andragogy in action. San Francisco: Jossey‐Bass; 1984.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

