Novel ribosome biogenesis-related biomarkers and therapeutic targets identified in psoriasis
- PMID: 40425712
- PMCID: PMC12116793
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03833-8
Novel ribosome biogenesis-related biomarkers and therapeutic targets identified in psoriasis
Abstract
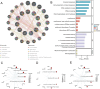
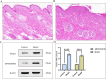
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease. Increasing evidence suggests a close association between ribosome biogenesis (RiboSis) and the pathogenesis of psoriasis. However, the precise mechanisms remain unclear. We first obtained bulk transcriptome and single-cell RNA sequencing datasets from the GEO database. Subsequently, differential expression analysis (DEG) and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were performed, preliminarily identifying 11 candidate biomarkers. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis revealed that these biomarkers are primarily involved in protein synthesis, regulation of gene expression, and control of the cell cycle and growth. Consensus clustering analysis combined with immune infiltration analysis revealed that the candidate biomarkers were strongly associated with innate immune cells, such as NK cells, mast cells, and monocytes, and were more closely linked to signaling pathways related to cell proliferation, cell cycle, inflammation, and glycolysis. From the 11 candidate biomarkers, we selected MPHOSPH6 and ISG20 (exhibiting the highest fold-changes) for external dataset validation, scRNA-seq analysis, and in vivo expression verification. Subsequently, potential therapeutic compounds targeting these biomarkers were predicted and validated via molecular docking. Collectively, our findings not only substantiate the critical role of RiboSis in psoriasis pathogenesis but also provide a framework for developing targeted therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Immune infiltration; Molecular docking; Psoriasis; Ribosome biogenesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The animal experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Sichuan Scientist Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (approval number: SYST-2024-003). The animal experiments described in this study were performed in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines ( https://arriveguidelines.org ). The publicly available human data applied in this study did not require ethical approval, as ethical approval and participant consent were obtained in the original study.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of shared biomarkers and drug repurposing in psoriasis and Crohn's disease: integrating bioinformatics, machine learning, and experimental approaches.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1587705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587705. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406126 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics combined with machine learning to analyze shared biomarkers and pathways in psoriasis and cervical squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 May 28;15:1351908. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1351908. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38863714 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing identifies POSTN as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis.Gene. 2024 Nov 30;928:148798. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148798. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Gene. 2024. PMID: 39067546
-
Identification of psoriasis-associated immune marker G3BP2 through single-cell RNA sequencing and meta analysis.Immunology. 2024 Dec;173(4):730-747. doi: 10.1111/imm.13851. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Immunology. 2024. PMID: 39267394
-
Identification of potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in psoriasis based on NF-κB pathway-related genes.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Mar 22;317(1):615. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-04017-0. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 40119934
References
-
- Pezzolo, E. & Naldi, L. Epidemiology of major chronic inflammatory immune-related skin diseases in 2019. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol.16, 155–166 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, A. W., Read, C. & Pathophysiology Clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: A review. JAMA323, 1945–1960 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

