Deep learning-based CAD system for Alzheimer's diagnosis using deep downsized KPLS
- PMID: 40425715
- PMCID: PMC12116745
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03010-x
Deep learning-based CAD system for Alzheimer's diagnosis using deep downsized KPLS
Abstract
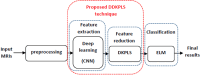
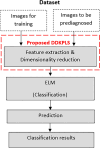
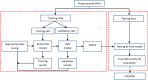
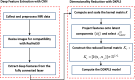
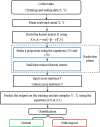
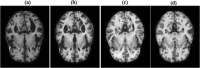
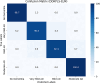
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent type of dementia. It is linked with a gradual decline in various brain functions, such as memory. Many research efforts are now directed toward non-invasive procedures for early diagnosis because early detection greatly benefits the patient care and treatment outcome. Additional to an accurate diagnosis and reduction of the rate of misdiagnosis; Computer-Aided Design (CAD) systems are built to give definitive diagnosis. This paper presents a novel CAD system to determine stages of AD. Initially, deep learning techniques are utilized to extract features from the AD brain MRIs. Then, the extracted features are reduced using a proposed feature reduction technique named Deep Downsized Kernel Partial Least Squares (DDKPLS). The proposed approach selects a reduced number of samples from the initial information matrix. The samples chosen give rise to a new data matrix further processed by KPLS to deal with the high dimensionality. The reduced feature space is finally classified using ELM. The implementation is named DDKPLS-ELM. Reference tests have been performed on the Kaggle MRI dataset, which exhibit the efficacy of the DDKPLS-based classifier; it achieves accuracy up to 95.4% and an F1 score of 95.1%.
Keywords: AD; Alzheimer’s disease; CAD system; DDKPLS; Deep learning; Feature reduction; KPLS.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang, F. et al. Multi-modal deep learning model for auxiliary diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurocomputing361, 185–195 (2019).
-
- Neffati, S., Ben Abdellafou, K., Aljuhani, A. & Taouali, O. An enhanced cad system based on machine learning algorithm for brain mri classification. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst.41, 1845–1854 (2021).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

