A wireless device for continuous measurement of brain parenchymal resistance tracks glymphatic function in humans
- PMID: 40425804
- PMCID: PMC12532611
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-025-01394-9
A wireless device for continuous measurement of brain parenchymal resistance tracks glymphatic function in humans
Abstract
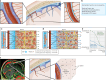
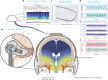
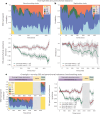
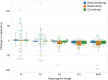
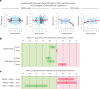
Glymphatic function in animal models supports the clearance of brain proteins whose mis-aggregation is implicated in neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. The measurement of glymphatic function in the human brain has been elusive due to invasive, bespoke and poorly time-resolved existing technologies. Here we describe a non-invasive multimodal device for the continuous measurement of sleep-active changes in parenchymal resistance in humans using repeated electrical impedance spectroscopy measurements in two separate clinical validation studies. Device measurements successfully paralleled sleep-associated changes in extracellular volume that regulate glymphatic function and predicted glymphatic solute exchange measured by contrast-enhanced MRI. We replicate preclinical findings showing that glymphatic function is increased with increasing sleep electroencephalogram (EEG) delta power and is decreased with increasing sleep EEG beta power and heart rate. The present investigational device permits the continuous and time-resolved assessment of parenchymal resistance in naturalistic settings necessary to determine the contribution of glymphatic impairment to risk and progression of Alzheimer's disease and to enable target-engagement studies that modulate glymphatic function in humans.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: P.D., L.G., S.R.L., J.W., T.S., M.M.L. and J.J.I. declare the existence of financial and stock options. Y.C. and R.M.K. declare the existence of financial competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

