The First Digital Strategy-Based Method for Training of Executive Functions: Impact on Cognition and Behavioral and Emotional Regulation, and Academic Success in Children With and Without Psychosocial Risk
- PMID: 40426411
- PMCID: PMC12109477
- DOI: 10.3390/bs15050633
The First Digital Strategy-Based Method for Training of Executive Functions: Impact on Cognition and Behavioral and Emotional Regulation, and Academic Success in Children With and Without Psychosocial Risk
Abstract
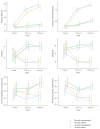
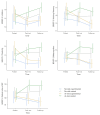
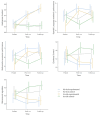
STap2Go is the first purely digital strategy-based method for the training of executive functions, making its evaluation relevant. This study assesses the effectiveness of this intervention in children with (at risk) and without (no-risk) psychosocial risk, which refers to socio-educational vulnerability, and examines whether its impact differs between groups. A total of 124 children (9-12 years old) were randomly assigned to either an experimental or an active control group. Individual assessments and family questionnaires were administered (FDT, WISC-V, RIST, BRIEF-2). Both groups received a 12-week intervention. The experimental group showed significant improvements in executive functions, processing speed, IQ, academic performance, and emotional and behavioral regulation compared to the controls. Notably, IQ, metacognition, and working memory continued improving at follow-up, suggesting lasting effects. While both groups benefited, the effects were more pronounced in at-risk children, particularly in BRIEF-2 (Inhibition, Metacognition, Behavioral Regulation) and academic performance in mathematics and language. Moreover, the psychosocial risk control group showed a trend toward deterioration over time. The far transfer achieved thanks to digital strategy-based training seems to have a greater effect on at-risk children, and can be used to compensate for their difficulties.
Keywords: children; children at psychosocial risk; cognitive training; executive functions; metacognition; strategy-based training.
Conflict of interest statement
T.R.-P. declares a conflict of interest as they are the designer of the Stap2go intervention. The other authors (D.C.-G. and M.V.R.) have no current or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The efficacy of a training that combines activities on working memory and metacognition: Transfer and maintenance effects in children with ADHD and typical development.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2019 Dec;41(10):1074-1087. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2019.1651827. Epub 2019 Aug 12. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2019. PMID: 31401917
-
The academic outcomes of working memory and metacognitive strategy training in children: A double-blind randomized controlled trial.Dev Sci. 2020 Jul;23(4):e12870. doi: 10.1111/desc.12870. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Dev Sci. 2020. PMID: 31134713 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Art of Learning - An Art-Based Intervention Aimed at Improving Children's Executive Functions.Front Psychol. 2019 Jul 31;10:1769. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01769. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31417476 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychological function in Tourette syndrome.Adv Neurol. 2001;85:103-11. Adv Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11530420 Review.
-
Working memory and executive functions: effects of training on academic achievement.Psychol Res. 2014 Nov;78(6):852-68. doi: 10.1007/s00426-013-0537-1. Epub 2014 Jan 4. Psychol Res. 2014. PMID: 24389706 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

