Staphylococcus aureus: A Review of the Pathogenesis and Virulence Mechanisms
- PMID: 40426537
- PMCID: PMC12108373
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics14050470
Staphylococcus aureus: A Review of the Pathogenesis and Virulence Mechanisms
Abstract
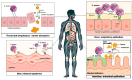
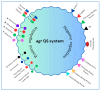
Staphylococcus aureus is a formidable human pathogen responsible for infections ranging from superficial skin lesions to life-threatening systemic diseases. This review synthesizes current knowledge on its pathogenesis, emphasizing colonization dynamics, virulence mechanisms, biofilm formation, and antibiotic resistance. By analyzing studies from PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, we highlight the pathogen's adaptability, driven by surface adhesins (e.g., ClfB, SasG), secreted toxins (e.g., PVL, TSST-1), and metabolic flexibility in iron acquisition and amino acid utilization. Nasal, skin, and oropharyngeal colonization are reservoirs for invasive infections, with biofilm persistence and horizontal gene transfer exacerbating antimicrobial resistance, particularly in methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). The review underscores the clinical challenges of multidrug-resistant strains, including vancomycin resistance and decolonization strategies' failure to target single anatomical sites. Key discussions address host-microbiome interactions, immune evasion tactics, and the limitations of current therapies. Future directions advocate for novel anti-virulence therapies, multi-epitope vaccines, and AI-driven diagnostics to combat evolving resistance. Strengthening global surveillance and interdisciplinary collaboration is critical to mitigating the public health burden of S. aureus.
Keywords: MRSA; Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic resistance; biofilm formation; colonization dynamics; metabolic adaptation; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Getaneh A. Staphylococcus aureus, ESKAPE Bacteria Challenging Current Health Care and Community Settings: A Literature Review. Clin. Lab. 2021;67 - PubMed
-
- Taylor T.A., Unakal C.G. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2025. [(accessed on 20 February 2025)]. Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441868/ - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

