Terbinafine Resistance in Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton indotineae: A Literature Review
- PMID: 40426539
- PMCID: PMC12108360
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics14050472
Terbinafine Resistance in Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton indotineae: A Literature Review
Abstract
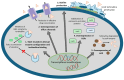
Background/objectives: Terbinafine has been the gold standard for the management of superficial fungal infections. The etiological agent generally is Trichophyton rubrum (T. rubrum); however, there has been increased reporting of a new terbinafine-resistant strain of the T. mentagrophytes complex (T. mentagrophytes ITS genotype VIII otherwise known as T. indotineae). Here, we review the epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of T. rubrum and T. indotineae infections.
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature search using PubMed, Embase (Ovid), and Web of Science, resulting in 83 qualified studies with data summarized for clinical features, antifungal susceptibility, and terbinafine resistance mechanisms and mutations.
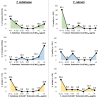
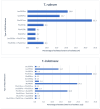
Results: Dermatophytosis is most commonly caused by T. rubrum; however, in certain parts of the world, especially in the Indian subcontinent, T. indotineae infections have been reported more frequently. The majority of T. rubrum isolates remain susceptible to terbinafine (over 60% of isolates show MIC50 and MIC90 < 0.5 µg/mL). In contrast, for T. indotineae, 30% of isolates exhibit MIC50 ≥ 0.5 µg/mL and 80% exhibit MIC90 ≥ 0.5 µg/mL. Frequently detected squalene epoxidase (SQLE) mutations in T. rubrum are Phe397Leu/Ile (41.6%) and Leu393Phe (20.8%); in T. indotineae, these include Phe397Leu (33.0%) and Ala448Thr (24.5%). Other potential terbinafine resistance mechanisms in T. rubrum and T. indotineae are discussed.
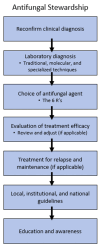
Conclusions: T. rubrum generally remain susceptible in vitro to terbinafine in contrast to T. indotineae. The essential components of an effective antifungal stewardship emphasize accurate clinical and laboratory diagnosis, susceptibility testing, and appropriate antifungal therapy selection with a multidisciplinary approach.
Keywords: Trichophyton indotineae; Trichophyton rubrum; antifungal drug resistance; squalene epoxidase; terbinafine.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors A.K.G., S., H.C.N., A.L., V.E. and T.W. were employed by Mediprobe Research Inc. The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of DermaGenius® resistance real-time polymerase chain reaction for rapid detection of terbinafine-resistant Trichophyton species.Mycoses. 2021 Jul;64(7):721-726. doi: 10.1111/myc.13271. Epub 2021 May 18. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 33760310
-
Increased terbinafine resistance among clinical genotypes of Trichophyton mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale species complex harboring squalene epoxidase gene mutations.J Mycol Med. 2024 Sep;34(3):101495. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2024.101495. Epub 2024 Jun 16. J Mycol Med. 2024. PMID: 38896927
-
Antifungal resistance in dermatophytes - review of the epidemiology, diagnostic challenges and treatment strategies for managing Trichophyton indotineae infections.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2024 Sep;22(9):739-751. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2024.2390629. Epub 2024 Aug 18. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2024. PMID: 39114868 Review.
-
Detection of terbinafine-resistant Trichophyton indotineae isolates within the Trichophyton mentagrophytes species complex isolated from patients in Hue City, Vietnam: A comprehensive analysis.Med Mycol. 2024 Aug 2;62(8):myae088. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myae088. Med Mycol. 2024. PMID: 39174488
-
Antifungal Resistance, Susceptibility Testing and Treatment of Recalcitrant Dermatophytosis Caused by Trichophyton indotineae: A North American Perspective on Management.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Nov;24(6):927-938. doi: 10.1007/s40257-023-00811-6. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37553539 Review.
Cited by
-
Significant Impact of Growth Medium on Itraconazole Susceptibility in Azole-Resistant Versus Wild-Type Trichophyton indotineae, rubrum, and quinckeanum Isolates.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 23;26(15):7090. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157090. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806222 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro susceptibility profiles of 16 antifungal drugs against Trichophyton indotineae.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0061825. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00618-25. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40548712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pathadka S., Yan V.K.C., Neoh C.F., Al-Badriyeh D., Kong D.C.M., Slavin M.A., Cowling B.J., Hung I.F.N., Wong I.C.K., Chan E.W. Global Consumption Trend of Antifungal Agents in Humans from 2008 to 2018: Data from 65 Middle- and High-Income Countries. Drugs. 2022;82:1193. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01751-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

