Impact of Flipped Classroom Instruction on Brain-Mediated Motor Skill Performance in University Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40426672
- PMCID: PMC12110293
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci15050501
Impact of Flipped Classroom Instruction on Brain-Mediated Motor Skill Performance in University Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates how the flipped classroom model-considered as a neurocognitive training environment-affects cognitive-motor integration and brain-mediated motor skill performance in university students, providing scientific evidence for optimizing higher-education physical education pedagogy (a course related to physical literacy and the cultivation of physical and mental health, rather than a training program for professional physical education teachers).
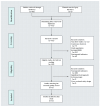
Methods: In order to compare the effects of flipped classroom and traditional teaching on the motor skill performance of university students, this study conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis according to PRISMA rules, whereby studies were screened according to specific inclusion criteria and data were extracted, assessed for quality, and then meta-analyzed to assess the effectiveness of the flipped classroom model in improving motor skill performance.
Results: A total of 12 original randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included in the study. The meta-analysis results indicated that the flipped classroom model significantly outperformed traditional teaching methods in improving university students' motor skill scores (standardized mean difference (SMD) = 1.22, 95% CI = 0.64-1.79, p < 0.0001). Subgroup analysis showed significant effects in both general major students and sports science major students, with no significant difference between studies conducted in China and those conducted in non-China regions.
Conclusions: The flipped classroom model demonstrates significant advantages over traditional PE teaching methods in improving motor skill performance. It enhances students' skill acquisition and classroom engagement, showing promising potential for future implementation in university PE programs. Further research should explore the model's applicability across different sports and student populations, as well as its long-term impact on skill retention and postgraduation sports participation.
Keywords: flipped classroom model; meta-analysis; physical education; sports performance; university education.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 7;19(3):e1339. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1339. eCollection 2023 Sep. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37425620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of flipped classrooms in Chinese baccalaureate nursing education: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Nurs Stud. 2018 Mar;79:94-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2017.11.012. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018. PMID: 29223013 Review.
-
The effectiveness of a flipped classroom on the development of Chinese nursing students' skill competence: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nurse Educ Today. 2019 Sep;80:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Nurse Educ Today. 2019. PMID: 31279251
-
Using a flipped classroom teaching and learning approach to promote scientific literacy skill development and retention.FEBS Open Bio. 2025 Mar;15(3):490-505. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13938. Epub 2024 Dec 3. FEBS Open Bio. 2025. PMID: 39625998 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxical effect of flipped classroom on nursing students' learning ability and satisfaction in a fundamental of nursing clinical course: A quasi-experimental study.J Prof Nurs. 2025 Mar-Apr;57:112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2025.01.011. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Prof Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40074373
References
-
- Gallahue D.L., Ozmun J.C. Understanding Motor Development: Infants, Children, Adolescents, Adults. 5th ed. McGraw-Hill; Dubuque, Iowa: 2002.
-
- Seefeldt V., Haubenstricker J. Patterns, Phases, or Stages: An Analytical Model for the Study of Developmental Movement. Wiley; New York, NY, USA: 1982.
-
- More P. The Vital Role of Physical Education and Sports in Holistic Development. J. Nov. Physiother. 2023;13:648.
-
- Justiz D.M. Donation of a Mexican House of Higher Education to the University of Las Tunas. [(accessed on 8 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.periodico26.cu/index.php/en/education-2/16103-donation-of-a-....
-
- Wibowo J., Krieger C., Gaum C., Dyson B. Bildung: A German Student-Centered Approach to Health and Physical Education. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2023;29:233–250. doi: 10.1177/1356336X221133060. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

