Life-Threatening Anemia and Thrombocytopenia in a Toddler with Influenza B: Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 40426810
- PMCID: PMC12110245
- DOI: 10.3390/children12050632
Life-Threatening Anemia and Thrombocytopenia in a Toddler with Influenza B: Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
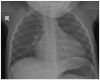
Background: Seasonal influenza viruses are primarily known for causing respiratory illness, but rare hematologic complications can occur, especially in young children. While influenza A is more commonly linked to severe manifestations, influenza B can similarly precipitate life-threatening cytopenias, particularly in toddlers. Case Presentation: We report the case of a previously healthy 1-year-and-8-months-old girl who presented with a high fever, cough, and marked pallor during peak influenza season. Laboratory tests revealed significant microcytic, hypochromic anemia and severe thrombocytopenia. Rapid antigen testing was positive for influenza B. An extensive workup for other causes of bicytopenia, including leukemia, hemolysis, aplastic anemia, and other viral infections, yielded negative results. The child was managed with urgent red blood cell and platelet transfusions, oseltamivir antiviral therapy, broad-spectrum antibiotics, corticosteroids, and supportive care. Bone marrow aspiration was deferred in light of the rapid hematologic recovery. Her hemoglobin greatly improved, and her platelet count reached normal values at discharge. Conclusions: Our case underscores the need to consider influenza in the differential diagnosis of unexplained cytopenias during flu season. This case illustrates that influenza B can mimic hematologic malignancies. Rapid diagnosis and supportive treatment are essential to avoid fatal outcomes. Influenza vaccination plays a significant role in preventing severe complications, such as those we encountered.
Keywords: anemia; influenza B virus; pediatrics; respiratory tract infections; thrombocytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiviral drugs in influenza: an adjunct to vaccination in some situations.Prescrire Int. 2006 Feb;15(81):21-30. Prescrire Int. 2006. PMID: 16548114
-
Influenza B presenting with bicytopenia in an adult - An unusual presentation and failure of antimicrobial stewardship by a practicing physician.J Family Med Prim Care. 2020 Jul 30;9(7):3737-3740. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_711_20. eCollection 2020 Jul. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020. PMID: 33102360 Free PMC article.
-
[Recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Work Group (GTEI) of the Spanish Society of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine and Coronary Units (SEMICYUC) and the Infections in Critically Ill Patients Study Group (GEIPC) of the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology (SEIMC) for the diagnosis and treatment of influenza A/H1N1 in seriously ill adults admitted to the Intensive Care Unit].Med Intensiva. 2012 Mar;36(2):103-37. doi: 10.1016/j.medin.2011.11.020. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Med Intensiva. 2012. PMID: 22245450 Spanish.
-
Hematologic complications of human immunodeficiency virus infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.Med Clin North Am. 1997 Mar;81(2):449-70. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(05)70526-5. Med Clin North Am. 1997. PMID: 9093237 Review.
-
Severe autoimmune cytopenias in treatment-naive hepatitis C virus infection: clinical description of 35 cases.Medicine (Baltimore). 2003 Mar;82(2):87-96. doi: 10.1097/00005792-200303000-00003. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003. PMID: 12640185 Review.
References
-
- Nair H., Brooks W.A., Katz M., Roca A., Berkley J.A., Madhi S.A., Simmerman J.M., Gordon A., Sato M., Howie S., et al. Global burden of respiratory infections due to seasonal influenza in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2011;378:1917–1930. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61051-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources