SpO2/FiO2 Correlates with PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) and Radiological Biomarkers of Severity: A Retrospective Study on COVID-19 Pneumonia Patients
- PMID: 40426900
- PMCID: PMC12108678
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051072
SpO2/FiO2 Correlates with PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) and Radiological Biomarkers of Severity: A Retrospective Study on COVID-19 Pneumonia Patients
Abstract
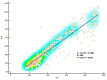
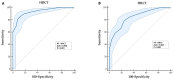
Background: In patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, the estimation of PaO2 represents the method of choice for monitoring a patient's oxygenation status and assessing disease severity. The aim of this study is, therefore, to investigate the correlation between SpO2/FiO2 and PaO2/FiO2, as well as radiological and laboratory biomarkers of severity. Methods: In this monocentric observational, analytical, retrospective large cohort study, consecutive patients with a confirmed diagnosis of pneumonia from SARS-CoV-2, hospitalized at the Cotugno Hospital-AORN dei Colli-of Naples, between 1 September 2020 and 28 February 2022 were considered for study inclusion. Patients with missing data were excluded. Results: We included 585 patients (median age 63 [22-95]). Mean PaO2/FiO2 was 203 [66-433], whilst mean SpO2/FiO2 was 240 [81-471]. We found that P/F ratio could be predicted from S/F ratio, as described by the linear regression equation (P/F = 13.273 + 0.790 × S/F). In addition, we found that SpO2/FiO2 ratio significantly correlated with HRCT score and laboratory markers of severity, including IL-6, D-Dimer, and NLR. Conclusions: SpO2/FiO2 ratio represents a highly useful resource as a valid surrogate of P/F ratio in patients with COVID pneumonia, also correlating with other biomarkers of severity, such as HRCT score and key laboratory markers.
Keywords: COVID-19; HRCT; SARS-CoV-2; SF ratio; SpO2/FiO2; laboratory biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Accuracy of PaO2 /FiO2 calculated from SpO2 for severity assessment in ED patients with pneumonia.Respirology. 2015 Jul;20(5):813-8. doi: 10.1111/resp.12560. Epub 2015 May 22. Respirology. 2015. PMID: 25998684
-
Comparison of non-invasive to invasive oxygenation ratios for diagnosing acute respiratory distress syndrome following coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a prospective derivation-validation cohort study.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018 Nov 27;13(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13019-018-0804-8. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018. PMID: 30482210 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygenation indices and early prediction of outcome in hypoxemic patients with COVID-19 pneumonia requiring noninvasive respiratory support in pulmonary intermediate care unit.Pneumonia (Nathan). 2024 Nov 25;16(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s41479-024-00145-9. Pneumonia (Nathan). 2024. PMID: 39582005 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of SpO2 to PaO2 based markers of lung disease severity for children with acute lung injury.Crit Care Med. 2012 Apr;40(4):1309-16. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31823bc61b. Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22202709
-
Rationale and limitations of the SpO2/FiO2 as a possible substitute for PaO2/FiO2 in different preclinical and clinical scenarios.Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022 Jan-Mar;34(1):185-196. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20220013-pt. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022. PMID: 35674526 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Idiopathic Retroperitoneal Hematoma Associated With Anticoagulation in a Patient With Moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Jul 6;17(7):e87395. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87395. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40772186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cascella M., Rajnik M., Aleem A., Dulebohn S.C., Di Napoli R. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2023. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19) - PubMed
-
- Wang H., Paulson K.R., Pease S.A., Watson S., Comfort H., Zheng P., Aravkin A.Y., Bisignano C., Barber R.M., Alam T., et al. Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020–2021. Lancet. 2022;399:1513–1536. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02796-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alberdi-Iglesias A., Martín-Rodríguez F., Ortega Rabbione G., Rubio-Babiano A.I., Núñez-Toste M.G., Sanz-García A., Del Pozo Vegas C., Castro Villamor M.A., Martín-Conty J.L., Jorge-Soto C., et al. Role of SpO2/FiO2 Ratio and ROX Index in Predicting Early Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in COVID-19. A Pragmatic, Retrospective, Multi-Center Study. Biomedicines. 2021;9:1036. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

