The Emerging Role and Mechanism of E2/E3 Hybrid Enzyme UBE2O in Human Diseases
- PMID: 40426910
- PMCID: PMC12109548
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051082
The Emerging Role and Mechanism of E2/E3 Hybrid Enzyme UBE2O in Human Diseases
Abstract
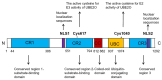
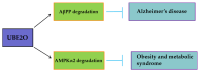
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) plays a pivotal role in determining protein fate, regulating signal transduction, and maintaining cellular homeostasis. Protein ubiquitination, a key post-translational modification, is orchestrated by the sequential actions of three primary enzymes, ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), and ubiquitin protein ligase (E3), alongside the regulatory influence of deubiquitinases (DUBs) and various cofactors. The process begins with E1, which activates ubiquitin molecules. Subsequently, E2 receives the activated ubiquitin from E1 and transfers it to E3. E3, in turn, recognizes specific target proteins and facilitates the covalent attachment of ubiquitin from E2 to lysine residues on the target protein. Among the E2 enzymes, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2O (UBE2O) stands out as a unique E2-E3 hybrid enzyme. UBE2O directly mediates the ubiquitination of a wide array of substrates, including 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 (AMPKα2), MAX interactor 1 (Mxi1), and v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog (c-Maf), among others. In this narrative review, we will explore the structural characteristics of UBE2O and elucidate its molecular functions. Additionally, we will summarize recent advancements in understanding the role of UBE2O in various tumors, Alzheimer's disease (AD), and metabolic diseases. Finally, we will discuss the potential of targeting UBE2O as a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of human diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; UBE2O; hematologic malignancies; metabolic diseases; solid tumors; substrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Perron T., Boissan M., Bièche I., Courtois L., Dingli F., Loew D., Chouchène M., Colasse S., Levy L., Prunier C. CYYR1 promotes the degradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 and is associated with favorable prognosis in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2024;300:107601. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107601. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

