Adipokines and Adipose Tissue: The Role and Use of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes or Heart Failure
- PMID: 40426925
- PMCID: PMC12108695
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051098
Adipokines and Adipose Tissue: The Role and Use of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes or Heart Failure
Abstract
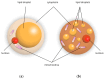
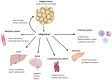
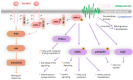
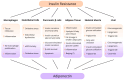
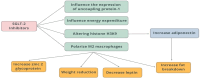
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors have become integral in treating both diabetes mellitus and heart failure, independent of left ventricular ejection fraction. Their pleiotropic effect influences multiple mechanisms, enhancing the function of various systems within the body. They exhibit nephroprotective and cardioprotective effects by improving cell metabolism, endothelial function, and slowing the fibrosis of the cardiac muscle, and they also have a beneficial impact on other organs. At the cellular level, they protect against the harmful effects of free radicals both by lowering glucose levels and by supporting the function of the antioxidant system. Moreover, SGLT-2 inhibitors can modify the metabolism of adipocytes by affecting the production of cytokines such as adiponectin-which increases insulin sensitivity, leading to weight loss and improved glycemic control.
Keywords: SGLT-2 inhibitors; adipokines; adiponectin; adipose tissue; flozins; heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

