Treatment of Advanced NSCLC Patients with an Anti-Idiotypic NeuGcGM3-Based Vaccine: Immune Correlates in Long-Term Survivors
- PMID: 40426949
- PMCID: PMC12109512
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051122
Treatment of Advanced NSCLC Patients with an Anti-Idiotypic NeuGcGM3-Based Vaccine: Immune Correlates in Long-Term Survivors
Abstract
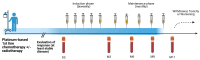
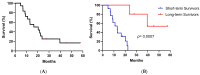
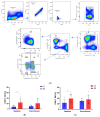
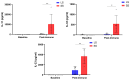
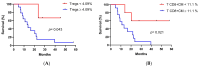
Background: Racotumomab-alum is an anti-idiotype vaccine targeting the NeuGcGM3 tumor-associated ganglioside. Clinical trials in advanced cancer patients have demonstrated low toxicity, high immunogenicity and clinical benefit. The goal of this study was to identify circulating biomarkers of clinical outcome. Methods: Eighteen patients with stage IIIb/IV non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were injected with racotumomab-alum as switch maintenance therapy after first-line chemotherapy. Treatment was administered until severe performance status worsening or toxicity. The frequencies of innate and adaptive lymphocytes were assessed by flow cytometry. Circulating factors were measured using multi-analyte flow assay kits. Results: The median overall survival was 16.5 months. Twenty-seven percent of patients were classified as long-term survivors. Patients with lower baseline frequencies of CD4+Tregs and central memory (CM) CD8+T cells displayed longer survival rates. Furthermore, higher baseline frequencies of NKT cells and a high CD8+T/CD4+Treg ratio were associated with longer survival. Interestingly, patients with significantly lower levels of effector memory (EM) CD8+T cells survived longer. The levels of NKT cells and terminal effector memory (EMRA) CD8+T cells were higher in long-term survivors in comparison with short-term survivors in post-immune samples. As expected, the ratio of CD8+T/CD4+Tregs showed significantly higher values during treatment in patients with clinical benefits. Regarding serum factors, pro-tumorigenic cytokines significantly increased during treatment in poor survivors. Conclusions: In advanced NSCLC patients receiving racotumomab-alum vaccine, longer survival could be associated with a unique profile of circulating lymphocyte subsets at baseline and during treatment. Additionally, certain pro-tumor-related cytokines increased in short-term survivors. These results should be confirmed in larger randomized clinical trials. This clinical trial was registered in the Cuban Clinical Trials Register (RPCE00000279).
Keywords: anti-idiotypic cancer vaccine; circulating biomarkers; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled clinical trial of racotumomab-alum vaccine as switch maintenance therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Jul 15;20(14):3660-71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1674. Epub 2014 May 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24788102 Clinical Trial.
-
Racotumomab-alum vaccine for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015 Jan;14(1):9-20. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.984691. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 25420897 Review.
-
Racotumomab - a novel anti-idiotype monoclonal antibody vaccine for the treatment of cancer.Drugs Today (Barc). 2014 Apr;50(4):301-7. doi: 10.1358/dot.2014.50.4.2116670. Drugs Today (Barc). 2014. PMID: 24918647 Review.
-
Anti-ganglioside antibodies induced in chickens by an alum-adsorbed anti-idiotype antibody targeting NeuGcGM3.Front Immunol. 2013 Jan 17;3:422. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00422. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23335925 Free PMC article.
-
Immune modulations during chemoimmunotherapy & novel vaccine strategies--in metastatic melanoma and non small-cell lung cancer.Dan Med J. 2013 Dec;60(12):B4774. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24355457 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

