Reduced Expression of UPRmt Proteins HSP10, HSP60, HTRA2, OMA1, SPG7, and YME1L Is Associated with Accelerated Heart Failure in Humans
- PMID: 40426970
- PMCID: PMC12108656
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051142
Reduced Expression of UPRmt Proteins HSP10, HSP60, HTRA2, OMA1, SPG7, and YME1L Is Associated with Accelerated Heart Failure in Humans
Abstract
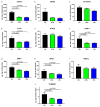
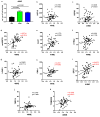
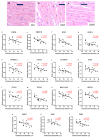
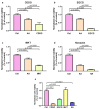
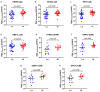
Background/Objectives: The mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) is one of the mitochondrial quality control mechanisms that is responsible for reparation and removal of damaged proteins in mitochondria. Methods: Here we investigated the role of the UPRmt in the myocardium of humans with and without heart failure and in the cell culture model. Results: The analysis of myocardial samples by ELISA from patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), as well as healthy donors, revealed a significantly reduced expression of the UPRmt proteins HSP10, CLPP, LONP1, OMA1, and SPG7 in patients with DCM and ICM. Furthermore, patients with DCM and ICM exhibited elevated levels of myocardial reactive oxygen species (ROS, tested by 4-hydroxynonenal) compared to controls, and a positive correlation between ROS production and mt-HSP70, OMA1, and SPG7 protein expression. The correlation analysis indicated a negative correlation between cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and the expression of several UPRmt genes. The inhibition of four tested UPRmt effector proteins exacerbated the injury of cultured cells under oxidative stress. The patients with ICM, DCM, or both, who showed lower myocardial expression of HSP10, HSP60, HTRA2, OMA1, SPG7, and YME1L, underwent heart transplantation or implantation of a left ventricular assist device earlier in life compared to those with the higher protein expression. Conclusions: In conclusion, our findings indicate that the reduced expression of several UPRmt effector proteins is associated with accelerated heart failure in patients, which, together with other results, indicates that impaired UPRmt may contribute to the pathogenesis of heart failure in humans.
Keywords: ROS; UPRmt; cardiomyopathy; heart; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arbelo E., Protonotarios A., Gimeno J.R., Arbustini E., Barriales-Villa R., Basso C., Bezzina C.R., Biagini E., Blom N.A., de Boer R.A., et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Cardiomyopathies: Developed by the Task Force on the Management of Cardiomyopathies of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. Heart J. 2023;44:3503–3626. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad194. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

