Redox Balance in Cancer in the Context of Tumor Prevention and Treatment
- PMID: 40426975
- PMCID: PMC12109055
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051149
Redox Balance in Cancer in the Context of Tumor Prevention and Treatment
Abstract
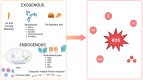
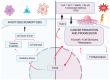
Malignant neoplasms constitute a substantial health concern for the human population, currently ranking as the second leading cause of mortality worldwide. In 2022, approximately 10 million deaths were attributable to cancer, and projections estimate that this number will rise to 35 million in 2050. Consequently, the development of effective cancer treatments and prevention strategies remains a primary focus of medical research. In this context, the impacts on the redox balance are being considered. The objective of this study was to present the current knowledge on oxidation and reduction processes in cancer. This review discloses the intricate and multifaceted interplay of oxidoreductive systems during carcinogenesis, which engenders discordant findings in the domain of tumor prevention and treatment. This study also examines the controversies surrounding the use of antioxidants, including their impact on other therapeutic interventions. The review offers a comprehensive overview of the existing knowledge on the subject, concluding that personalized and precise anticancer therapies targeting the redox processes can serve as both effective diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
Keywords: antioxidants; cancer; diagnosis; oxidants; prevention; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small-molecule redox modulators with anticancer activity: A comprehensive mechanistic update.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Nov 20;209(Pt 2):211-227. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.10.406. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37898387 Review.
-
Tuberculosis.In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. PMID: 30212088 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic AMPK signaling dynamic activation in response to REDOX balance are sentinel biomarkers of exercise and antioxidant intervention to improve blood glucose control.Elife. 2022 Sep 26;11:e79939. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79939. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36155132 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour Immunotherapy and Applications of Immunological Products: A Review of Literature.J Immunol Res. 2024 Oct 24;2024:8481761. doi: 10.1155/2024/8481761. eCollection 2024. J Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39483536 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

