Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Narrative Review of Diagnostic Advances and Emerging Therapies
- PMID: 40427056
- PMCID: PMC12109326
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051230
Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Narrative Review of Diagnostic Advances and Emerging Therapies
Abstract
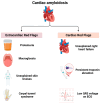
Background/Objectives: Cardiac amyloidosis (CA) is an underdiagnosed and potentially life-threatening infiltrative cardiomyopathy characterized by the extracellular deposition of misfolded amyloid fibrils in cardiac tissue. It is most commonly associated with light-chain (AL) amyloidosis and transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis, either hereditary or wild-type. The disease often presents with non-specific symptoms, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. This study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the pathophysiology, diagnostic strategies, and current therapeutic approaches for cardiac amyloidosis, with a focus on improving early detection and clinical outcomes. Methods: A narrative review was conducted using databases such as PubMed and Scopus, covering the period from September 2016 to March 2025. Keywords such as "cardiac amyloidosis", "cardiac amyloidosis from transthyretin", "cardiomyopathy", "transthyretin", "immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis", and "familial amyloidosis" were used. Relevant clinical trials and guideline-based management recommendations were also included. Results: This review highlights that non-invasive imaging modalities and serum biomarker analyses are key to reducing diagnostic delays. New therapeutic developments, including gene-editing technologies and RNA-based therapies, show promise in early trials. Multidisciplinary management and increased awareness are crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment optimization. Conclusions: The early recognition of cardiac amyloidosis remains a major clinical challenge. Advances in non-invasive diagnostics and emerging disease-modifying therapies are transforming the prognosis of affected patients. Continued research and heightened clinical suspicion are essential to improve outcomes in this complex and heterogeneous disease.
Keywords: TTR; amyloidosis; cardiac amyloidosis; diagnosis; transthyretin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Benson M.D., Buxbaum J.N., Eisenberg D.S., Merlini G., Saraiva M.J.M., Sekijima Y., Sipe J.D., Westermark P. Amyloid Nomenclature 2018: Recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) Nomenclature Committee. Amyloid. 2018;25:215–219. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2018.1549825. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous