Bioinformatics-Guided Experimental Validation Identifies NQO1 as a Senescence-Ferroptosis Hub in Liver Fibrosis
- PMID: 40427075
- PMCID: PMC12108982
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13051249
Bioinformatics-Guided Experimental Validation Identifies NQO1 as a Senescence-Ferroptosis Hub in Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
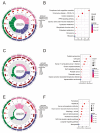
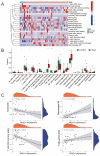
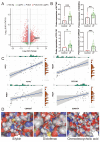
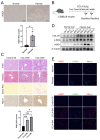
Background: As a pivotal point for the development of liver diseases, liver fibrosis (LF) is closely associated with cellular senescence and ferroptosis. However, there is a lack of effective markers that accurately predict LF status. This study aims to identify key genes involved in LF through bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation. Methods: We used bioinformatics analysis of Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) data to investigate the gene functions, prognostic value, and immune associations of characteristic genes in LF. Functional enrichment analysis of DEGs was performed using GO and KEGG. Immune cell types and their proportions were estimated with CIBERSORTx. In addition, we analyzed the role of NQO1 in LF using IHC, WB, PCR, and flow cytometry. Results: Bioinformatics analysis identified 10 hub genes, including AR, CDKN1A, GJA1, CTSB, HIF1A, HMGB1, NQO1, PARP1, PTEN, and TXN. Among them, NQO1 was strongly correlated with immune cell activity. Experimental validation confirmed that NQO1 is upregulated and promotes αSMA and COL1A1 expression in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Knockdown of NQO1 significantly affected the proliferation of HSCs. Conclusions: NQO1 plays a critical role in HSC senescence and ferroptosis, promoting HSC activation and contributing to LF progression. Our findings suggest that NQO1 may serve as a potential biomarker for LF.
Keywords: NQO1; biomarkers; cellular senescence; ferroptosis; immune cells; liver fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of STAT3 as a biomarker for cellular senescence in liver fibrosis: A bioinformatics and experimental validation study.Genomics. 2024 Mar;116(2):110800. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2024.110800. Epub 2024 Jan 28. Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38286349
-
MEOX2 Participates in Hepatic Stellate Cells-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Regulating the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Discov Med. 2024 Jun;36(185):1199-1209. doi: 10.24976/Discov.Med.202436185.110. Discov Med. 2024. PMID: 38926106
-
Identifying immune cell infiltration and effective diagnostic biomarkers in Crohn's disease by bioinformatics analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 9;14:1162473. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1162473. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37622114 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in the effect of ferroptosis of HSCs on the development of liver fibrosis.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Sep 26;10:1258870. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1258870. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37860583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JUN and ATF3 in Gout: Ferroptosis-related potential diagnostic biomarkers.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 30;10(22):e39957. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39957. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39619595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

