Neurotrophins as Potential Biomarkers for Active Disease and Poor Outcome in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 40427122
- PMCID: PMC12110685
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17101623
Neurotrophins as Potential Biomarkers for Active Disease and Poor Outcome in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
Background: Neurotrophins (NTs) are pivotal growth factors in cellular development and survival. Their precise implications in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) remain unclear.
Methods: Pediatric ALL samples (2011-2021) were analyzed from a Southern Brazil cohort. Neurotrophin levels were quantified via ELISA, with survival analysis using Kaplan-Meier curves. Gene expression data were sourced from public genomic repositories and analyzed with R software version 4.0.5.
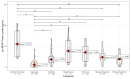
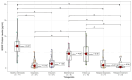
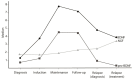
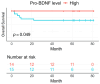
Results: At diagnosis, pro-BDNF, BDNF, and NGF levels were significantly lower than in healthy controls. Reduced pro-BDNF correlated with unfavorable outcomes. NGF and sortilin were highly expressed in healthy samples, while BDNF and p75NTR were predominant in T-ALL and B-ALL, respectively.
Conclusions: Neurotrophins show significant alterations in the tumor microenvironment of pediatric ALL. Further studies are needed to elucidate their precise role and prognostic potential.
Keywords: ALL; BDNF; childhood leukemia; neurotrophins; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

