Effect of GnRHR, BMP6 and FSHR Gene Pyramiding on Litter Traits of Goats
- PMID: 40427236
- PMCID: PMC12108322
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15101358
Effect of GnRHR, BMP6 and FSHR Gene Pyramiding on Litter Traits of Goats
Abstract
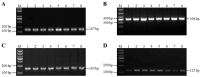
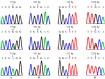
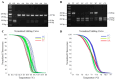
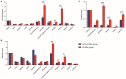
Many studies have shown that only a few breeds of goat have the trait of high fertility, and genes play an important role in regulating litter size. This study investigated the effects of GnRHR, BMP6, and FSHR gene polymorphisms on litter traits in four goat breeds (Chongqing black, Chuanzhong black, Leizhou, and Nubian). Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (g.75G > A in GnRHR, g.951T > C in BMP6, and g.-112C > T/g.3236C > A in FSHR) were genotyped using PCR-RFLP/HRM in 959 goats. Association analysis revealed significant correlations between these SNPs and litter size in the Chongqing, Chuanzhong, and Leizhou breeds, with genotypes AA (GnRHR), CC (BMP6), TT (FSHR), and AA (FSHR) linked to higher prolificacy. Polygene polymerizing effect analysis identified the optimal combinations (e.g., AATTCC, AACCAACC) with enhanced litter sizes. Tissue-specific qPCR in Chuanzhong goats showed GnRHR, BMP6, and FSHR were significantly more highly expressed in reproductive tissues (pituitary, breast, ovary, oviduct) of the prolific group than those in the non-prolific group. These SNPs serve as potential molecular markers for improving goat litter traits through polygenic selection, emphasizing the synergistic impact of multi-gene interactions on prolificacy.
Keywords: BMP6; FSHR; GnRHR; litter size; pyramiding effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

