Ferroptosis and Iron Homeostasis: Molecular Mechanisms and Neurodegenerative Disease Implications
- PMID: 40427409
- PMCID: PMC12108473
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14050527
Ferroptosis and Iron Homeostasis: Molecular Mechanisms and Neurodegenerative Disease Implications
Abstract
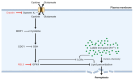
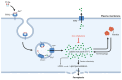
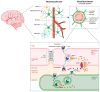
Iron dysregulation has emerged as a pivotal factor in neurodegenerative pathologies, especially through its capacity to promote ferroptosis, a unique form of regulated cell death driven by iron-catalyzed lipid peroxidation. This review synthesizes current evidence on the molecular underpinnings of ferroptosis, focusing on how disruptions in iron homeostasis interact with key antioxidant defenses, such as the system Xc--glutathione-GPX4 axis, to tip neurons toward lethal oxidative damage. Building on these mechanistic foundations, we explore how ferroptosis intersects with hallmark pathologies in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) and examine how iron accumulation in vulnerable brain regions may fuel disease-specific protein aggregation and neurodegeneration. We further surveyed the distinct components of ferroptosis, highlighting the role of lipid peroxidation enzymes, mitochondrial dysfunction, and recently discovered parallel pathways that either exacerbate or mitigate neuronal death. Finally, we discuss how these insights open new avenues for neuroprotective strategies, including iron chelation and lipid peroxidation inhibitors. By highlighting open questions, this review seeks to clarify the current state of knowledge and proposes directions to harness ferroptosis modulation for disease intervention.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; cell death; ferroptosis; iron homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W., et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

