A Highly Potent Apomorphine Derivative Enhancing Neurite Outgrowth via Nrf2 Activation
- PMID: 40427418
- PMCID: PMC12108180
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14050537
A Highly Potent Apomorphine Derivative Enhancing Neurite Outgrowth via Nrf2 Activation
Abstract
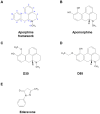
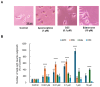
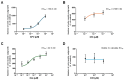
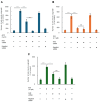
Apomorphine (APO), a dopamine agonist, activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and exerts antioxidant effects, making it a promising candidate for neuroprotection against oxidative stress. This study evaluated neuroplasticity-enhancing properties of newly synthesized APO derivatives, focusing on their ability to promote neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells under nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulation. D55, an APO derivative, retains the hydroxyl group at APO's 11th position while substituting the 10th with an ethoxy group. D55 exhibited the highest potency (EC50 = 0.5661 nM), significantly enhancing neurite outgrowth. APO demonstrated the highest efficacy (Emax ~10-fold increase), while edaravone (Eda) required higher concentrations (EC50 = 22.5 nM) for moderate effects (Emax ~4-fold increase). D30, in which the 11th hydroxyl was replaced with a methoxy group, had no effect. Neurite outgrowth-promoting effects of APO, D55, and Eda were significantly attenuated by Nrf2 siRNA knockdown, confirming that their neuroplasticity effects are Nrf2-mediated. These findings confirm that D55 is a highly potent Nrf2-activating compound with strong neuroprotective potential, providing new insights into its therapeutic applications for neurodegenerative diseases associated with oxidative stress.
Keywords: Nrf2 activation; apomorphine derivatives; edaravone; neurite outgrowth; neurodegenerative diseases; therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
- im0210625h0001, 17ek0109270s0301, 21ek0109511h0001, 22ek0109511h0002, 23ek0109511h0003, and 24ek0109625s0602/Rare/Intractable Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JP21am0101120/the Platform Project for Supporting Drug Discovery and Life Science Research (Basis for Sup-porting Innovative Drug Discovery and Life Science Research (BINDS)) from AMED
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

