A Novel Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) Formulation Mitigates Sleep Deprivation-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model
- PMID: 40427603
- PMCID: PMC12109121
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15050710
A Novel Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) Formulation Mitigates Sleep Deprivation-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model
Abstract
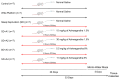
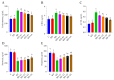
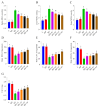
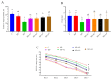
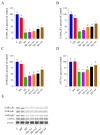
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a well-known adaptogenic herb traditionally used to enhance sleep quality and mitigate stress-induced cognitive decline. This study investigated the effects of different doses of ashwagandha root extract (AE) formulations on cognitive function, oxidative stress, and neuronal plasticity in a rat model of sleep deprivation (SD). Forty-nine rats were randomly assigned to seven groups: control, wide platform (WP), SD, SD + A1 (15 mg/kg AE 1.5%), SD + A2 (30 mg/kg AE 1.5%), SD + A3 (5.5 mg/kg AE 8.0%), and SD + A4 (11 mg/kg AE 8.0%). The extract was administered orally for four weeks. SD induced via a modified wide platform model significantly impaired spatial memory, increased oxidative stress, and suppressed GABA receptor activity. Treatment with all AE doses, except 15 mg/kg AE 1.5%, considerably reduced serum corticosterone (12% for SD + A2, 15% for SD + A3, and 32% for SD + A4), CRH (11% for SD + A2, 14% for SD + A3, and 17% for SD + A4), ACTH (22% for SD + A2, 26% for SD + A3, and 38% for SD + A4), and MDA levels (31% for SD + A2, 34% for SD + A3, and 46% for SD + A4) (p < 0.05). All doses improved antioxidant enzyme activity and memory performance, while AE 8.0% doses notably increased serotonin (19% for SD + A3 and 33% for SD + A4) and dopamine levels (40% for SD + A3 and 50% for SD + A4). Moreover, AE treatment enhanced markers of neuronal plasticity and partially improved GABAergic function. These findings suggest that AE formulations, particularly at higher concentrations, exert neuroprotective effects against SD-induced cognitive impairment by modulating oxidative stress, neurotransmitter balance, and neuroplasticity, indicating their potential application in managing stress-related neurological disorders.
Keywords: GABAergic pathway; ashwagandha; memory; sleep deprivation; stress; withanolides.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M.M. and M.P. are employees of OmniActive Health Technologies, which funded this research. The funders had no role in the design, execution, or analysis of this study. Independent validation of data integrity was conducted to ensure unbiased results. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Taylor T.L., Fernandez E.J., Handley K.N., Hazel S.J. Non-Pharmacological Interventions for the Treatment of Canine Cognitive Dysfunction: A Scoping Review. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2023;269:106097. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2023.106097. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

