Large Language Models in Genomics-A Perspective on Personalized Medicine
- PMID: 40428059
- PMCID: PMC12108693
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12050440
Large Language Models in Genomics-A Perspective on Personalized Medicine
Abstract
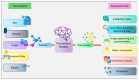
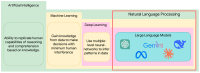
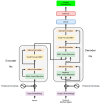
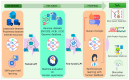
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI), particularly large language models (LLMs), into the healthcare industry is revolutionizing the field of medicine. LLMs possess the capability to analyze the scientific literature and genomic data by comprehending and producing human-like text. This enhances the accuracy, precision, and efficiency of extensive genomic analyses through contextualization. LLMs have made significant advancements in their ability to understand complex genetic terminology and accurately predict medical outcomes. These capabilities allow for a more thorough understanding of genetic influences on health issues and the creation of more effective therapies. This review emphasizes LLMs' significant impact on healthcare, evaluates their triumphs and limitations in genomic data processing, and makes recommendations for addressing these limitations in order to enhance the healthcare system. It explores the latest advancements in LLMs for genomic analysis, focusing on enhancing disease diagnosis and treatment accuracy by taking into account an individual's genetic composition. It also anticipates a future in which AI-driven genomic analysis is commonplace in clinical practice, suggesting potential research areas. To effectively leverage LLMs' potential in personalized medicine, it is vital to actively support innovation across multiple sectors, ensuring that AI developments directly contribute to healthcare solutions tailored to individual patients.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI); genomic data; large language models (LLMs); precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Large Language Models in Transforming Emergency Medicine: Scoping Review.JMIR Med Inform. 2024 May 10;12:e53787. doi: 10.2196/53787. JMIR Med Inform. 2024. PMID: 38728687 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing Health Care: The Transformative Impact of Large Language Models in Medicine.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 7;27:e59069. doi: 10.2196/59069. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39773666 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing large language models for gastroenterology research: a conceptual framework.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 1;18:17562848251328577. doi: 10.1177/17562848251328577. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40171241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Application of Large Language Models in Gastroenterology: A Review of the Literature.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;16(19):3328. doi: 10.3390/cancers16193328. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large Language Models and User Trust: Consequence of Self-Referential Learning Loop and the Deskilling of Health Care Professionals.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Apr 25;26:e56764. doi: 10.2196/56764. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 38662419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marques L., Costa B., Pereira M., Silva A., Santos J., Saldanha L., Silva I., Magalhães P., Schmidt S., Vale N. Advancing Precision Medicine: A Review of Innovative In Silico Approaches for Drug Development, Clinical Pharmacology and Personalized Healthcare. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16:332. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030332. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 62462021/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 25JCXK006YB/Philosophy and Social Sciences Planning Project of Zhejiang Province
- 2025A1515010197/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- HNJG2024ZD-16/Hainan Province Higher Education Teaching Reform Project
- 2021YFB2700600/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

