Revolutionizing Utility of Big Data Analytics in Personalized Cardiovascular Healthcare
- PMID: 40428082
- PMCID: PMC12108848
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12050463
Revolutionizing Utility of Big Data Analytics in Personalized Cardiovascular Healthcare
Abstract
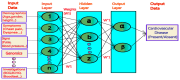
The term "big data analytics (BDA)" defines the computational techniques to study complex datasets that are too large for common data processing software, encompassing techniques such as data mining (DM), machine learning (ML), and predictive analytics (PA) to find patterns, correlations, and insights in massive datasets. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are attributed to a combination of various risk factors, including sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes, dyslipidaemia, and hypertension. We searched PubMed and published research using the Google and Cochrane search engines to evaluate existing models of BDA that have been used for CVD prediction models. We critically analyse the pitfalls and advantages of various BDA models using artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and artificial neural networks (ANN). BDA with the integration of wide-ranging data sources, such as genomic, proteomic, and lifestyle data, could help understand the complex biological mechanisms behind CVD, including risk stratification in risk-exposed individuals. Predictive modelling is proposed to help in the development of personalized medicines, particularly in pharmacogenomics; understanding genetic variation might help to guide drug selection and dosing, with the consequent improvement in patient outcomes. To summarize, incorporating BDA into cardiovascular research and treatment represents a paradigm shift in our approach to CVD prevention, diagnosis, and management. By leveraging the power of big data, researchers and clinicians can gain deeper insights into disease mechanisms, improve patient care, and ultimately reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease on individuals and healthcare systems.
Keywords: big data analytics; cardiovascular diseases; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implications of Big Data Analytics, AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning in the Health Care System of Bangladesh: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Oct 28;26:e54710. doi: 10.2196/54710. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39466315 Free PMC article.
-
How can Big Data Analytics Support People-Centred and Integrated Health Services: A Scoping Review.Int J Integr Care. 2022 Jun 16;22(2):23. doi: 10.5334/ijic.5543. eCollection 2022 Apr-Jun. Int J Integr Care. 2022. PMID: 35756337 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of AI in Cardiovascular Event Monitoring and Early Detection: Scoping Literature Review.JMIR Med Inform. 2025 Mar 6;13:e64349. doi: 10.2196/64349. JMIR Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40048151 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing diabetic retinopathy screening and management: The role of artificial intelligence and machine learning.World J Clin Cases. 2025 Feb 16;13(5):101306. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i5.101306. World J Clin Cases. 2025. PMID: 39959767 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Biomarkers for Early Detection and Risk Stratification of Cardiovascular Diseases-A Literature Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 May 26;8(5):e70878. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70878. eCollection 2025 May. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40432692 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Machine Learning-Powered Smart Healthcare Systems in the Era of Big Data: Applications, Diagnostic Insights, Challenges, and Ethical Implications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 30;15(15):1914. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15151914. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804880 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim D.S., Park J.W. Medical big data: Promise and challenges. [(accessed on 14 September 2024)];Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2017 36:3–11. Available online: https://www.krcp-ksn.org/journal/view.php?id=10.23876/j.krcp.2017.36.1.3. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Heart Association. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources