Early Dynamics of Circulating Tumor DNA Following Curative Hypofractionated Radiotherapy Related to Disease Control in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 40428191
- PMCID: PMC12109695
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15101198
Early Dynamics of Circulating Tumor DNA Following Curative Hypofractionated Radiotherapy Related to Disease Control in Lung Cancer
Abstract
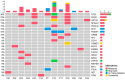
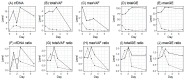
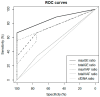
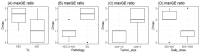
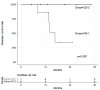
Background/objectives: We aimed to characterize the dynamic pattern of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) during hypofractionated radiation therapy (RT) in patients with lung cancer and assess its clinical relevance. Metholds: Prospectively, 24 patients diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer underwent curative RT with 60-64 Gy in 4-20 fractions. Blood samples were collected at baseline (D0) and on post-RT days 1-3 and 7 (D1-3 and D7). The ctDNA was longitudinally analyzed using LiquidSCAN. To find a feasible index associated with outcome, total VAF(%), max VAF(%), total GE (hGE/mL) and max GE (hGE/mL), were evaluated. Results: Thirteen patients with available samples were analyzed with a median 22.2-month follow-up (range, 5.2-34.3 months). Four patients experienced progression between 7.9 and 16.6 months after RT (PD group), and the nine presented no evidence of disease (NED group). The Dmax, the day with the highest ctDNA level among D0-7, was significantly different between the groups with total GE and max GE (p = 0.035 and 0.021, respectively). According to the ROC curves, the max GE showed the best AUC (86.1%) and the cut-off value of the Dmax was 1.5 (sensitivity: 66.7%, specificity: 100%, positive-predictive value: 100%, and negative-predictive value: 57.1%). Tumor size ≥ 3 cm, squamous histology, and a daily dose 3-4 Gy were correlated with the Dmax = D2-3. The Dmax showed better disease control rate with marginal significance (p = 0.081). Conclusions: The timing of early ctDNA elevation may have the potential to predict RT response. The max GE may be an index to verify the ctDNA levels after RT.
Keywords: cell-free DNA; liquid biopsy; lung cancer; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[18F-FDG PET/CT Metabolic Parameters and Circulating Tumour DNA Mutation Abundance in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Correlation and Survival Analysis].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Dec;31(6):1690-1700. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2023.06.014. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38071047 Chinese.
-
Prognostic value of circulating tumour DNA during post-radiotherapy surveillance in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Transl Med. 2022 Nov;12(11):e1116. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1116. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36437506 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant Osimertinib Followed by Sequential Definitive Radiation Therapy and/or Surgery in Stage III Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Study.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023 Sep 1;117(1):105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.03.042. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023. PMID: 36925073 Clinical Trial.
-
Using Liquid Biopsy to Predict Relapse After Radiotherapy in Squamous Cell Head-Neck and Esophageal Cancer.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023 Jul 3;3(4):403-410. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10232. eCollection 2023 Jul-Aug. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023. PMID: 37405217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of radiation therapy in treatment of adults with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline update.J Neurooncol. 2020 Nov;150(2):215-267. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03612-7. Epub 2020 Nov 19. J Neurooncol. 2020. PMID: 33215344
Cited by
-
The prognostic and predictive value of peripheral immune-related proteins in patients with lung cancer treated with radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 17;15:1625212. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1625212. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40746594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosenlund L., Guldbrandsen K., Ahlborn L.B., Bloch M., Skougaard K., Albrecht-Beste E., Nellemann H.M., Krakauer M., Gortz P.M., Fledelius J., et al. ctDNA can detect minimal residual disease in curative treated non-small cell lung cancer patients using a tumor agnostic approach. Lung Cancer. 2025;203:108528. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2025.108528. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

