Automated Cell Counting in CSF Diagnostics Revisited-Friend or Foe?
- PMID: 40428195
- PMCID: PMC12109621
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15101202
Automated Cell Counting in CSF Diagnostics Revisited-Friend or Foe?
Abstract
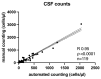
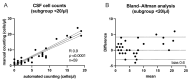
Background/Objectives: The gold standard for cerebrospinal fluid leukocyte counting is manual counting in a Fuchs-Rosenthal chamber. Recent advances in automated body-fluid-counting systems, offering a time- and labor-saving solution, are challenging this dogma. Yet, the equivalence of diagnostic accuracy is still debated in the community. Methods: We compared manual and automated cell counting of cerebrospinal fluid samples of lumbar punctures and extraventricular drains with both low and high leukocyte counts, shedding light on the variability of results between man and machine. Results: Automated and manual cell counting showed a strong correlation across all samples, particularly in the subgroup of patients with fewer than 20 cells/µl, where outliers could become especially clinically relevant. Conclusions: We found the automated counting system to be highly accurate and not lacking in diagnostic sensitivity even at low cell counts, making it a powerful tool when used in the right clinical setting.
Keywords: CSF diagnostics; Fuchs–Rosenthal counting chamber; Sysmex XN-9000; automated cell counting; cerebrospinal fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automated vs. manual cerebrospinal fluid cell counts: a work and cost analysis comparing the Sysmex XE-5000 and the Fuchs-Rosenthal manual counting chamber.Int J Lab Hematol. 2011 Dec;33(6):629-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-553X.2011.01339.x. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Int J Lab Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21668655
-
Evaluation of the XE-5000 for the automated analysis of blood cells in cerebrospinal fluid.Clin Biochem. 2009 May;42(7-8):684-91. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2009.01.025. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Clin Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19233149
-
A New Automated Technology for Cerebrospinal Fluid Cell Counts: Comparison of Accuracy and Clinical Impact of GloCyte, Sysmex XN, and Manual Methods.Am J Clin Pathol. 2017 May 1;147(5):507-514. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqx026. Am J Clin Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28419185
-
Automated Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cells Using Commercially Available Blood Cell Analysis Devices-A Critical Appraisal.Cells. 2021 May 18;10(5):1232. doi: 10.3390/cells10051232. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34069775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical relevance and contemporary methods for counting blood cells in body fluids suspected of inflammatory disease.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015 Oct;53(11):1689-706. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2014-1247. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015. PMID: 25879321 Review.
References
-
- Aune M.W., Becker J.L., Brugnara C., Canfield W., Dorfman D.M., Fiehn W., Fischer G., Fitzpatrick P., Flaming T.H., Henriksen H.K., et al. Automated flow cytometric analysis of blood cells in cerebrospinal fluid: Analytic performance. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004;121:690–700. doi: 10.1309/EKFW9E3LLFXE15X9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

