The Train-Line Pattern on Duplex Ultrasound Helps Differentiate Intramural Thrombus from Atheromatous Plaque in Common Carotid Artery Dissection
- PMID: 40428291
- PMCID: PMC12110014
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15101297
The Train-Line Pattern on Duplex Ultrasound Helps Differentiate Intramural Thrombus from Atheromatous Plaque in Common Carotid Artery Dissection
Abstract
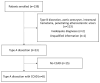
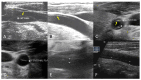
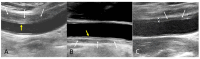
Background/Objectives: Common carotid artery dissection (CCAD) can result in severe neurological sequelae; however, its diagnosis may be challenging due to consciousness disturbance and aphasia. The objective of this article is to propose a new imaging feature to assist in the identification of CCAD. Methods: This retrospective case series enrolled 139 patients with discharge diagnoses of aortic dissection who underwent carotid ultrasound during admission over a period of three years. Results: Among these patients, 23 had type A aortic dissection, and 113 had type B aortic dissection or related conditions. Notably, among the 23 patients with type A aortic dissection, eight had associated common carotid artery dissection (CCAD), and a total of nine CCAD events were identified. Meanwhile, a B-mode ultrasound revealed six double lumens with intimal flaps and three intramural thrombi. The 'train-line' pattern in ultrasonography was discerned by detecting a hypoechoic thickened wall, which was characterized by a margin formed by two parallel linear reflections in close proximity. This distinctive "train-line" pattern was identified in three intimal flaps and two intramural thrombi. Conclusions: While double lumens and intramural thrombus are prevalent findings, the latter may be misinterpreted as atherosclerotic plaque. The "train-line" pattern may aid in distinguishing intramural thrombus from atheromatous plaque, offering an additional diagnostic tool alongside the identification of double lumens with intimal flaps.
Keywords: aortic dissection; carotid duplex sonography; common carotid artery dissection; neuroimaging; stroke diagnosis; train-line pattern.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hagan P.G., Nienaber C.A., Isselbacher E.M., Bruckman D., Karavite D.J., Russman P.L., Evangelista A., Fattori R., Suzuki T., Oh J.K., et al. The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): New insights into an old disease. JAMA. 2000;283:897–903. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.7.897. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

