Sustainable Extraction of Actinostemma lobatum Kernel Oil by 2-Methyltetrahydrofuran: A Comparative Study on Physicochemical Properties and Bioactive Compounds Against Petro-Sourced Solvents
- PMID: 40428462
- PMCID: PMC12111321
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14101682
Sustainable Extraction of Actinostemma lobatum Kernel Oil by 2-Methyltetrahydrofuran: A Comparative Study on Physicochemical Properties and Bioactive Compounds Against Petro-Sourced Solvents
Abstract
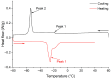
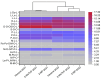
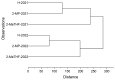
This study aims to evaluate the effect of extraction solvent type on the physicochemical properties and bioactive compounds of Actinostemma lobatum Maxim. kernel oil for two successive harvest years. Oils were extracted using the bio-based solvent 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF) and conventional petroleum-derived solvents (n-hexane and 2-methylpentane). Results indicated that 2-MeTHF achieved significantly higher oil yields (27.60% in 2021 and 29.77% in 2022) compared to n-hexane and 2-methylpentane. Unfortunately, 2-MeTHF-extracted oils exhibited greater susceptibility to oxidation, displaying elevated levels of primary and secondary oxidation products relative to other solvents. Meanwhile, 2-methylpentane-extracted oil showed a relatively high oxidative stability index. In addition, differential scanning calorimetry results also aligned with the oxidative status. Further variance analysis revealed that the harvest year exerted a more pronounced impact on fatty acid and triacylglycerol profiles than the solvent type. Additionally, tocopherols and tocotrienols were abundant, with β- and δ-tocopherols predominating. 2-MeTHF-extracted oils harvested in 2022 contained the highest total tocols (1118.83 mg/kg) among all samples. Also, phytosterols were detected, with β-sitosterol constituting the predominant compound. Furthermore, the 2-MeTHF-extracted oils contained higher β-carotene contents compared to other samples. These above findings concluded that 2-MeTHF is a good alternative to conventional solvents for extracting of A. lobatum kernel oil.
Keywords: 2-Methyloxolane; Actinostemma lobatum kernel oil; bioactive compounds; harvest year; solvent type; thermal property; tocotrienols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Green Solvent to Substitute Hexane for Bioactive Lipids Extraction from Black Cumin and Basil Seeds.Foods. 2021 Jun 28;10(7):1493. doi: 10.3390/foods10071493. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34203148 Free PMC article.
-
Green extraction of oil from Carum carvi seeds using bio-based solvent and supercritical fluid: Evaluation of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.Phytochem Anal. 2020 Jan;31(1):37-45. doi: 10.1002/pca.2864. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Phytochem Anal. 2020. PMID: 31313408
-
Green solvent 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF) improves recovery of bioactive molecules from oilseeds and prevents lipid peroxidation in oils.Food Chem. 2025 Jun 30;478:143659. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143659. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40049128
-
2-Methyloxolane (2-MeOx) as Sustainable Lipophilic Solvent to Substitute Hexane for Green Extraction of Natural Products. Properties, Applications, and Perspectives.Molecules. 2020 Jul 28;25(15):3417. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153417. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32731508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2-Methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF): a biomass-derived solvent with broad application in organic chemistry.ChemSusChem. 2012 Aug;5(8):1369-79. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201100780. ChemSusChem. 2012. PMID: 22887922 Review.
References
-
- Zheng L., Zhang T., Xie L., Karrar E., Shi L., Jin J., Wang X., Jin Q. Physicochemical characteristics of Actinostemma lobatum Maxim. kernel oil by supercritical fluid extraction and conventional methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020;152:112516. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112516. - DOI
-
- Beltrán G., Bucheli M.E., Aguilera M.P., Belaj A., Jimenez A. Squalene in virgin olive oil: Screening of variability in olive cultivars. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016;118:1250–1253. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201500295. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

