Advancements in Wearable and Implantable BioMEMS Devices: Transforming Healthcare Through Technology
- PMID: 40428648
- PMCID: PMC12113605
- DOI: 10.3390/mi16050522
Advancements in Wearable and Implantable BioMEMS Devices: Transforming Healthcare Through Technology
Abstract
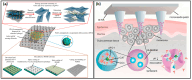
Wearable and implantable BioMEMSs (biomedical microelectromechanical systems) have transformed modern healthcare by enabling continuous, personalized, and minimally invasive monitoring, diagnostics, and therapy. Wearable BioMEMSs have advanced rapidly, encompassing a diverse range of biosensors, bioelectronic systems, drug delivery platforms, and motion tracking technologies. These devices enable non-invasive, real-time monitoring of biochemical, electrophysiological, and biomechanical signals, offering personalized and proactive healthcare solutions. In parallel, implantable BioMEMS have significantly enhanced long-term diagnostics, targeted drug delivery, and neurostimulation. From continuous glucose and intraocular pressure monitoring to programmable drug delivery and bioelectric implants for neuromodulation, these devices are improving precision treatment by continuous monitoring and localized therapy. This review explores the materials and technologies driving advancements in wearable and implantable BioMEMSs, focusing on their impact on chronic disease management, cardiology, respiratory care, and glaucoma treatment. We also highlight their integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), paving the way for smarter, data-driven healthcare solutions. Despite their potential, BioMEMSs face challenges such as regulatory complexities, global standardization, and societal determinants. Looking ahead, we explore emerging directions like multifunctional systems, biodegradable power sources, and next-generation point-of-care diagnostics. Collectively, these advancements position BioMEMS as pivotal enablers of future patient-centric healthcare systems.
Keywords: bioMEMS; biocompatible materials; cardiac monitoring; chronic disease management; drug delivery; healthcare monitoring; implantable devices; point of care; societal determinants; wearable medical devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Erdem A., Eksin E., Senturk H., Yildiz E., Maral M. Recent developments in wearable biosensors for healthcare and biomedical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024;171:117510. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117510. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

