Exploring the Link Between Vitamin K and Depression: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40428819
- PMCID: PMC12113079
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61050861
Exploring the Link Between Vitamin K and Depression: A Systematic Review
Abstract
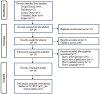
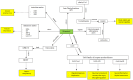
Background and Objectives: Depression is a multifactorial mental health disorder involving inflammation, oxidative stress, neuroplasticity deficits, and metabolic dysfunction. Emerging research suggests that vitamin K, beyond its classical roles in coagulation and bone metabolism, may influence neurobiological processes relevant to mood regulation. This systematic review evaluates the association between vitamin K and depressive symptoms and explores potential underlying mechanisms. Materials and Methods: A systematic search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, following PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Eligible studies included human or animal research examining associations between vitamin K status (dietary intake or serum levels) and depression-related outcomes. Fourteen studies met the inclusion criteria: eleven observational studies, one randomized controlled trial (RCT), and two preclinical animal studies. Results: Most observational studies reported an inverse association between vitamin K intake or serum levels and depressive symptoms across diverse populations. One small RCT demonstrated modest improvements in depression scores following vitamin K2 (menaquinone-7) supplementation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Two preclinical studies using non-depression models reported behavioral improvements and reduced oxidative stress following vitamin K2 administration. Conclusions: While preliminary findings suggest a potential role for vitamin K in pathways relevant to depression, the current evidence is limited by cross-sectional designs, lack of isoform-specific analyses, and the absence of depression-focused preclinical models. Mechanisms including inflammation reduction, oxidative stress modulation, sphingolipid regulation, and vitamin K-dependent protein signaling (e.g., GAS6 and osteocalcin) were discussed based on indirect evidence and require further investigation in depression-specific contexts.
Keywords: depression; neuroinflammation; osteocalcin; oxidative stress; vitamin K.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Depressive Disorder (Depression) [(accessed on 31 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression/?gad_source=....
-
- Evans-Lacko S., Aguilar-Gaxiola S., Al-Hamzawi A., Alonso J., Benjet C., Bruffaerts R., Chiu W.T., Florescu S., de Girolamo G., Gureje O., et al. Socio-economic variations in the mental health treatment gap for people with anxiety, mood, and substance use disorders: Results from the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) surveys. Psychol. Med. 2018;48:1560–1571. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717003336. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zainal Abidin Z., Kamaruddin N.S., Hein Z.M., Che Mohd Nassir C.M.N., Ramli M.D.C. The Gut-Brain Axis and Depression: Understanding Microbiota-Driven Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Preprints. 2025. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous