Stress Behaviour of an Immature Maxillary Central Incisor: A 3D Finite Element Analysis
- PMID: 40429045
- PMCID: PMC12113038
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18102305
Stress Behaviour of an Immature Maxillary Central Incisor: A 3D Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
Background and objective: Immature maxillary incisors (IMIs) are especially susceptible to failure due to their thin dentinal walls and compromised structural integrity following endodontic treatment. This study aims to evaluate the stress distribution within the root dentin after various post-endodontic treatments.
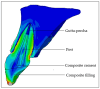
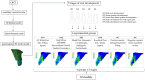
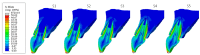
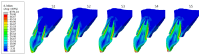
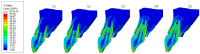
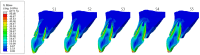
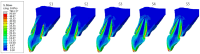
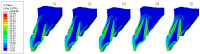
Materials and methods: A personalized finite element analysis model of IMI was created using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) data. Based on data from the literature, five stages of root development were reconstructed: half root development (S1), three-quarter development (S2), more than three-quarter development (S3), fully developed root with open apex (S4), and fully developed root with closed apex (S5). Six experimental groups were analyzed: GC Fiber Post (PS1); RelyX Post (PS2); metal post Unimetric 1.0 (PS3); everStick Post (PS4); positive control group with only the gutta-percha filling (PC), and intact maxillary incisor as negative control group (NC). The resulting equivalent stresses were evaluated using the Hencky-von Mises (HMH) strength theory.
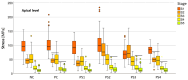
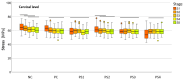
Results: The mean HMH stress within the root dentin was statistically significantly higher at the cervical level in all stages, except in stage S1 and models PS2 and PS3 in stage S2, where it was significantly higher at the apical level (p < 0.001 for all models, except stage S3 [PC model p < 0.005; NC model p < 0.008]). The PS4 model showed the lowest stress values at the cervical level in stages S1, S2, and S3 (55.19 MPa, 58.78 MPa, 58.84 MPa) and the PS1 model in stages S4 and S5 (57.48 MPa, 58.81 MPa). At the apical level, model PS3 showed the lowest stress values in stage S1 (69.60 MPa), model PS1 in stages S2, S3, and S5 (35.99 MPa, 44.30 MPa, 12.51 MPa) and model PC in stage S4 (17.85 MPa).
Conclusions: The results showed that the greatest stress in an immature maxillary central incisor occurred at the cervical level, except during the early stage of root development. Post placement did not reduce root dentin stress.
Keywords: finite element analysis; maxillary central incisor; post-endodontic treatment; root dentin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jadhav K., Vaidya M.J., Hegde V., Kawle S. Management of non-vital immature teeth: A review. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2021;20:35–40. doi: 10.9790/0853-2007093540. - DOI
-
- de Andrade G., Saavedra G., Augusto M., Alfonzo G., Brandão H., Tribst J., Dal Piva A. Post-endodontic restorative treatments and their mechanical behavior: A narrative review. Dent. Rev. 2023;3:100067. doi: 10.1016/j.dentre.2023.100067. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

