The Role of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Athletic Individuals-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40429571
- PMCID: PMC12112729
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14103576
The Role of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Athletic Individuals-A Narrative Review
Abstract
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an advanced cardiac imaging modality that is often required when evaluating athletic individuals. Unrestricted imaging planes, excellent spatial resolution, and a lack of ionising radiation are some of the benefits of this modality. Cardiac MRI has been established as the gold standard imaging modality for morphological assessment, volumetric analysis, and tissue characterisation. Cardiac MRI without any doubt is an excellent diagnostic tool when evaluating athletes with symptoms or those individuals exhibiting equivocal findings at screening. It is also useful for athletes who fall within the grey zone and is especially important among athletes with a suspected or confirmed diagnosis. Cardiac MRI plays a strategic role when adopting a shared decision-making model in athletes with heart disease, tailoring and personalising medical care to the condition and the athlete's wishes. The aim of this review is to provide a comprehensive yet practical overview of the role of cardiac MRI when evaluating athletes in clinic.
Keywords: athlete; cardiac MRI; cardiomyopathy; fibrosis; sudden cardiac death.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

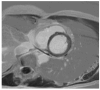
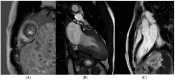
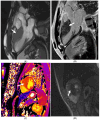
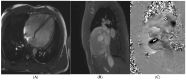
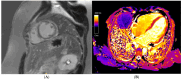
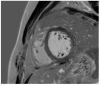

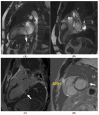
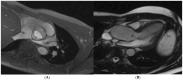
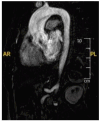
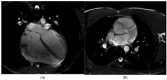
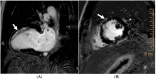
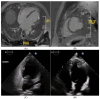
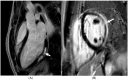
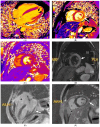
References
-
- WHO . Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. [(accessed on 24 January 2025)]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK566046/
-
- Ljungqvist A., Jenoure P.J., Engebretsen L., Alonso J.M., Bahr R., Clough A.F., de Bondt G., Dvorak J., Maloley R., Matheson G., et al. The International Olympic Committee (IOC) Consensus Statement on Periodic Health Evaluation of Elite Athletes, March 2009. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2009;43:631–643. doi: 10.1097/jsm.0b013e3181b7332c. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

