Role of Masticatory Force in Modulating Jawbone Immunity and Bone Homeostasis: A Review
- PMID: 40429623
- PMCID: PMC12111287
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104478
Role of Masticatory Force in Modulating Jawbone Immunity and Bone Homeostasis: A Review
Abstract
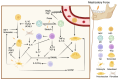
Mastication exerts a significant influence on both the structural and immunological environment of the jawbone. The mechanical stress generated during chewing initiates bone remodeling through the coordinated activities of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, with these processes being modulated by immune cell responses. This review summarizes the interaction between masticatory forces and jawbone immunity, focusing on key mechanisms such as mechanotransduction in osteocytes, macrophage polarization, and the activation of T cells. The review also delves into the role of the receptor activator of nuclear factor κ-B ligand (RANKL), receptor activator of nuclear factor κ-B (RANK), and osteoprotegerin (OPG) signaling pathway, highlighting its critical function in bone resorption and immune regulation. Additionally, the review summarizes how masticatory forces modulate the immune response through changes in immune cells, particularly focusing on cytokines, and the involvement of hormonal and molecular pathways. These findings provide valuable insights into the complex interplay between mechanical forces and immune cells, with implications for bone health.
Keywords: jawbone immunity; masticatory force; mechanotransduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Osteocyte-Mediated Translation of Mechanical Stimuli to Cellular Signaling and Its Role in Bone and Non-bone-Related Clinical Complications.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020 Feb;18(1):67-80. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00564-9. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020. PMID: 31953640 Review.
-
Osteoimmunology in orthodontic tooth movement.Oral Dis. 2015 Sep;21(6):694-704. doi: 10.1111/odi.12273. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Oral Dis. 2015. PMID: 25040955 Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of RANKL presentation to osteoclast precursors.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014 Mar;12(1):115-20. doi: 10.1007/s11914-014-0189-0. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014. PMID: 24477414 Review.
-
Local Production of Osteoprotegerin by Osteoblasts Suppresses Bone Resorption.Cell Rep. 2020 Sep 8;32(10):108052. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108052. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32905775 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 Jan;39(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01162-6. Epub 2020 Oct 20. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 33079279 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Grant NO. 2022YFC2504200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 82470936/the National Nature Science Foundation of China
- CSA-SIS2022-11/Young Clinical Research Fund of the Chinese Stomatological Association
- PX2023054/the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program
- YSP202105/the Beijing Stomatological Hospital, Capital Medical University Young Scientist Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

