Sobrerol Improves Memory Impairment in the Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia Mouse Model
- PMID: 40429757
- PMCID: PMC12111148
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104613
Sobrerol Improves Memory Impairment in the Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia Mouse Model
Abstract
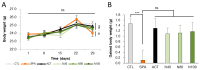
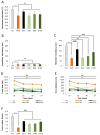
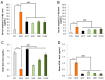
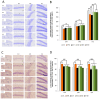
Memory impairment is a defining characteristic of Alzheimer's disease (AD), with amnesia often appearing as its earliest symptom. Given the multifactorial nature of AD pathogenesis, this study investigates the multi-target therapeutic potential of sobrerol (coded as NRM-331) in a scopolamine-induced amnesia mouse model, focusing specifically on its effects in ameliorating memory deficits and enhancing neuronal plasticity. Sixty male C57BL/6NCrljOri mice were divided into six groups (10 mice/group): vehicle control (CTL, saline), scopolamine (SPA, 10 mg/kg/day), Aricept (APT, 2 mg/kg/day), and three treatment groups receiving NRM-331 at doses of 40, 80, and 100 mg/kg/day. Several behavioral tests were conducted, including the Y-maze test, passive avoidance test, and Morris water maze test. Additionally, biochemical assays were performed in serum (to measure Aß 1-40 and Aß 1-42) and in the brain (to assess ACh and AChE levels), along with histopathological examination of the brain using Nissl staining and p-tau IHC. No significant change was observed in the Y-maze test or the acquisition trial of the passive avoidance test. However, improvements were noted in the retention trial of the passive avoidance test and the Morris water maze test (including escape latency, swim distance, and number of platform crossed) for the NRM-331 groups compared to the SPA group. Serum levels of Aß 1-40 and Aß 1-42 decreased in the NRM-331 groups compared to the SPA group. In the brain, levels of ACh significantly increased, while AChE levels significantly decreased compared to the SPA group. The number of neuronal cells improved in the CA1, CA3, and DG regions of the hippocampus, as indicated by Nissl staining. A significant reduction in p-tau accumulation was also observed in the NRM-331 groups. In conclusion, NRM-331 demonstrated an anti-amnesic effect by enhancing hippocampal cholinergic signaling, alongside exhibiting anti-tau and anti-Aβ synthesis properties. These therapeutic effects suggest that NRM-331 significantly mitigates memory impairment induced by SPA through a neuroprotective mechanism.
Keywords: acetylcholine; amnesia; amyloid beta; memory; phospho-tau; scopolamine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employed by the company NeurolMed. The authors declare no conflict of interests related to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cortico-hippocampal memory enhancing activity of hesperetin on scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice: role of antioxidant defense system, cholinergic neurotransmission and expression of BDNF.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Aug;34(4):979-989. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-00409-0. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 30949953
-
Cajanus cajan (L) Millsp. seed extract ameliorates scopolamine-induced amnesia through increase in antioxidant defense mechanisms and cholinergic neurotransmission.Niger J Physiol Sci. 2023 Jun 30;38(1):91-99. doi: 10.54548/njps.v38i1.13. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38243363
-
Terminalia chebula extract prevents scopolamine-induced amnesia via cholinergic modulation and anti-oxidative effects in mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 May 2;18(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2212-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29716575 Free PMC article.
-
Fat-1 expression enhance hippocampal memory in scopolamine-induced amnesia.J Nutr Biochem. 2020 Aug;82:108394. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108394. Epub 2020 Apr 8. J Nutr Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32454411
-
Euonymus hamiltonianus Extract Improves Amnesia in APPswe/Tau Transgenic and Scopolamine-Induced Dementia Models.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Dec;61(12):10845-10860. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04242-0. Epub 2024 May 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38801629
References
-
- Tannenbaum C., Paquette A., Hilmer S., Holroyd-Leduc J., Carnahan R. A systematic review of amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment induced by anticholinergic, antihistamine, GABAergic and opioid drugs. Drugs Aging. 2012;29:639–658. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

